News
Run 71 (General module) and C15 (Companion module) were accomplished April to July 2024.
Below, find a short summary of the results observed. Click on the epitope name to see the complete and detailed assessment report for the individual markers evaluated. In each assessment report, NordiQC intended to identify best practice methods and recommendable immunohistochemical critical assay performance controls (iCAPCs) to both guide the IHC protocol set-up and to monitor the IHC performance within the laboratories.
As specified previously, we do encourage participants to update the submitted protocol settings and reagents used if changed from initial data of entry. Protocols can be updated until the slide return deadline. The submitted data are used to analyze the overall performance and identify root causes for both inferior and optimal performance.
General module - run 71
BAP1: 224 laboratories participated in this second assessment and obtained a pass rate of 63% (25% optimal) being slightly reduced compared to the first run 65, 2022. The relatively low pass rate was in particular caused by lack of reproducibility of the IHC assays for BAP1.
CD20: 428 laboratories participated and obtained a relatively high pass rate of 85% (73% optimal). This was the fourth NordiQC assessment of CD20 and the pass rate decreased significantly compared to the previous run 35, 2012. 97% used the mAb clone L26 either as concentrated or RTU format. The RTU systems from Leica Biosystems and Ventana/Roche provided an impressive pass rate of 100% applying vendor recommended protocol settings. The reduced pass rate was especially related to an inferior pass rate of the Dako/Agilent RTU system for Omnis used by 18% of all participants with an overall low pass rate of 42%.
CD117: 428 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 94% (71% optimal) being at the highest level in all runs for CD117. The main parameters contributing to the positive development have in this and the latest runs been related to the extended use of robust primary rmAb clones YR145 and EP10 on the expense of the less successful Abs as pAb 4502 and especially the rmAb clone 9.7. Throughout the different assessment runs a harmonization of the protocol settings has been observed. While previously omission of HIER or HIER in low pH buffers were frequently applied, now virtually all protocols are based on HIER in high pH buffers.
CK-PAN: 410 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 70% (50% optimal). The mAb clone cocktail AE1/AE3 either as “single” cocktail or in combination with other clones was used by 92% of the participants. The performance of the cocktails was highly influenced by choice of pre-treatment method, IHC platform and “AE1/AE3 vendor”.
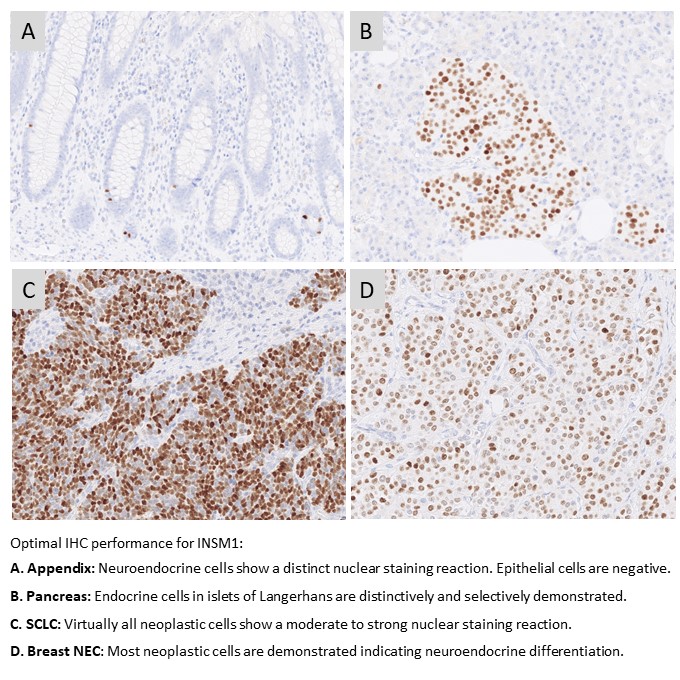
INSM1: 156 laboratories participated in this first assessment of INSM1 with a pass rate of 72% (35% optimal). The assessment focused on INSM1 for the diagnostic work-up in the identification of neuroendocrine differentiation in neoplasias. The most cited and in this assessment widely used mAb clone A-8 gave a pass rate of 55%, when used as a concentrate. A low reproducibility was observed as identical protocols gave both sufficient and insufficient results. The mAb clone MRQ-70 was found superior providing a pass rate of 93% and 94% when used as concentrated or RTU format, respectively.
PMS2: 380 laboratories participated in this fourth assessment of PMS2 and obtained a pass rate of 63% (35% optimal). 85% of the participants used RTU systems for PMS2. The RTU systems from Dako/Agilent and Leica Biosystems based on the rmAb clone EP51 were most successful giving a pass rate of 96% and 100%, respectively applying vendor recommended protocol settings. In contrast an inferior pass rate of 32% was observed for the widely used Ventana/Roche RTU system based on mAb clone A16-4.
Companion module - run C15
PD-L1 TPS/CPS (KEYTRUDA®): 255 laboratories participated being the highest level till now and a very satisfactory pass rate of 88% was observed. Similar to the observations seen in previous runs, the insufficient PD-L1 IHC results were most frequently characterized by a too low TPS/CPS level changing PD-L1 status in one or more of the carcinomas included. The PD-L1 IHC assay, 22C3 GE006, Dako/Agilent applied in concordance to vendor recommended guidelines, was most successful providing a pass rate of 100%, with an optimal rate of 97%. The Ventana/Roche SP263 assay provided a pass rate of 92%, 48% optimal and improved compared to the level in run C14.
PD-L1 IC score (TECENTRIQ®): 146 laboratories participated and a relatively low pass rate of 68% was observed, however slightly increased compared to the level seen in the previous run. The assessment for PD-L1 IC score focused on the evaluation of the analytical accuracy of the PD-L1 IHC assays for urothelial carcinomas and TNBCs. The insufficient results were characterized by either pure false negative results (seen for SP142 based assays), false positive results (seen for non-SP142 based assays) or an extensive staining reaction in tumour cells compromising the evaluation of PD-L1 reaction in immune cell. In concordance with previous runs, the Ventana/Roche PD-L1 SP142 IHC assays 741-4860 and 790-4860 were most successful providing a pass rate of 92% and 95%, respectively.
July 10th 2024
Søren Nielsen
Scheme director

Run 70 (General module), B37 (breast module), and H25 (HER2 ISH module) were accomplished from February to April 2024. In total, about 500 laboratories from more than 50 countries participated in at least one of the modules offered, and about 3.200 slides were assessed.
As usual, a short summary of the results is given below. Click on the epitope name to see the complete and detailed assessment report for the individual markers evaluated. In each assessment report, NordiQC intended to identify best practice methods and recommendable immunohistochemical critical assay performance controls (iCAPCs) to both guide the IHC protocol set-up and to monitor the IHC performance within the laboratories.
As specified previously, we do encourage participants to update the submitted protocol settings and reagents used if changed from initial data of entry. The submitted data are used to analyze the overall performance and identify root causes for both inferior and optimal performance.
Due to the relatively low pass rate, GATA3 and p53 will be repeated in 2025 and reassessment will not be available.
General module - run 70:
Bcl-6: 373 laboratories participated and obtained a relatively low pass rate of 70% (35% optimal). The mAb clones PG-B6p and LN22 provided the highest proportion of sufficient and optimal results applied as an RTU format (Dako/Agilent (Omnis) and Leica Biosystems, respectively). The RTU system based on the mAb clone GI191E/A8 (Ventana/Roche) provided a lower pass rate and was challenged by poor signal-to-noise ratio and false positive results. In a concentrated format, mAb clone GI191E/A8 obtained similar pass rate as the mAb clones PG-B6p and LN22.
CGA: 369 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 75% (40% optimal). An increased pass rate was observed compared to the previous run 67 and back to the level seen in run 53. The mAb clone LK2H10 was most widely used and very successful and in particular as RTU from Ventana/Roche. In concordance with previous assessments for CGA, the mAb clones DAK-A3 and 5H7 were found less successful and cannot be recommended.
GATA3: 390 laboratories participated and obtained a low pass rate of 65% (40% optimal). This was the fourth assessment of GATA3 in NordiQC and focused on the application in the diagnostic work-up of cancers of unknown primary origin. The vast majority of participants used the mAb clone L50-823. Used within a LD assay, optimal results could be obtained on all main fully automated IHC platforms. The Ventana/Roche RTU system based on clone L50-823 gave the highest pass rate and proportion of optimal results. Due to the relatively low pass rate, GATA3 will be repeated in 2025 and reassessment will not be available.
p53: 396 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 65% (16% optimal). This was the sixth assessment of p53 in NordiQC, and the fourth using more challenging assessment criteria introduced in run 63, 2021, focusing on IHC for p53 to demonstrate different TP53 mutations in endometrial carcinomas. The pass rate was identical to the latest run 67 being 65% (29% optimal). The widely used mAbs clones BP53-11 and DO-7 could both be used to provide optimal results providing the protocols were based on efficient HIER in an alkaline buffer and of central importance in combination with a 3-step detection system. As a consequence of the “new purpose of p53 IHC” the most important parameter being a careful calibration of the primary Ab to consistently identify p53 in low-level expressing structures as dispersed normal lymphocytes and stromal cells being of central importance in the diagnosis of carcinomas with loss of p53 expression. Due to the relatively low pass rate, p53 will be repeated in 2025 and reassessment will not be available.
PRAME: 259 laboratories participated and a pass rate of 78% was observed (44% optimal). This was the second assessment for PRAME in NordiQC, and a slightly improved pass rate was obtained, compared to 73% (38% optimal) in the last run. The assessment focused again on PRAME being used in the diagnostic work-up in the differential diagnosis between malignant melanoma and benign melanocytic lesions. The most widely used rmAb clone EPR20330 proved to be most robust with a pass rate of 80%, 44% optimal and provided optimal results on all the main automated IHC platforms (Dako/Agilent, Leica Biosystems and Ventana/Roche). Both false negative and false positive results were observed.
Breast module - run B37:
Estrogen receptor (ER): 426 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 85% (35% optimal) being increased to the latest assessment, but still slightly reduced to the level seen previously. In concordance to previously, too weak or false negative staining reactions were the predominant features of insufficient results. The widely used rmAb clones SP1 and EP1 and mAb clone 6F11 could all be used to provide an optimal result. 91% of the participants used RTU systems for the demonstration of ER. The RTU system from Dako/Agilent based on clone EP1 for Omnis was most successful providing a pass rate of 96%. Tonsil was found to be recommendable as positive and negative tissue control.
HER2 IHC: 405 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 89% (57% optimal) being slightly increased compared to run B36 and similar to the level observed in runs B35. In this assessment, the recently launched 2’ generation HercepTest™ Dako/Agilent for Omnis was most successful providing a pass rate of 100%. The well-established CE-IVD approved HER2 IHC assays PATHWAY® and HER2 4B5, Ventana/Roche gave a slightly lower pass rate of 91% and 87% respectively, compared to 95% and 94% in run B36 when applied as recommended by vendor. LD assays based on a concentrate or RTU with no predictive claim were used by 18% of participants giving a pass rate of 73% (31% optimal). The insufficient results were primarily caused by false negative results, whereas a minor proportion caused by either an increased proportion of positive cells or an excessive cytoplasmic staining reaction compromising the read-out.
Progesterone receptor (PR): 420 laboratories participated and a pass rate of 93% (71% optimal) was observed being virtual identical to the level seen in the last four runs. mAb clones 16, PgR 636, PgR 1294 and rmAb clone 1E2 could all be used to provide optimal results. 88% of the participants used RTU systems and obtained a pass rate of 95%. In this assessment, too weak or false negative staining reactions were the predominant features of insufficient results. Tonsil and uterine cervix in combination are recommendable negative and positive tissue controls.
HER2 ISH module - H25:
HER2 ISH: 161 laboratories participated in the technical assessment of HER2 ISH (BRISH) and obtained a pass rate of 85% (45% optimal) and being the highest pass rate seen in the HER2 ISH in the last decade. The improvement was primarily related to the changed assessment criteria from run H24, allowing large negative areas of >25% providing the individual tissue cores still could be evaluated with confidence. The VENTANA HER2 Dual ISH DNA Probe Cocktail, 800-6043 was used by 94% of the participants either as single assay or in combination with HER2 IHC. The insufficient results were typically characterized by large negative areas in one or more of the breast carcinoma samples compromising the evaluation of HER2 gene status, but also caused by impaired morphology, generally weak or missing signals.
213 laboratories participated in the HER2 ISH scoring module and the consensus rate was 91%.
April 28th 2024
Søren Nielsen
Scheme director

Run 69 (General module), B36 (breast module), C14 (Companion module) and H24 were accomplished from October to December 2023. In total, about 500 laboratories from more than 40 countries participated in at least one of the modules offered, and about 3.200 slides were assessed.
As usual, a short summary of the results is given below. Click on the epitope name to see the complete and detailed assessment report for the individual markers evaluated. In each assessment report, NordiQC intended to identify best practice methods and recommendable immunohistochemical critical assay performance controls (iCAPCs) to both guide the IHC protocol set-up and to monitor the IHC performance within the laboratories.
As specified previously, we do encourage participants to update the submitted protocol settings and reagents used if changed from initial data of entry. The submitted data are used to analyze the overall performance and identify root causes for both inferior and optimal performance.
Please be aware that we now have opened for protocol submission for the Winter run: General module run 70, Breast module run B37 and HER2 ISH module H25.
General module - run 69
CD5: 379 laboratories participated and obtained a relatively low pass rate of 72% (54% optimal). Several antibody clones could be used to obtain an optimal result. The rmAb clone SP19 proved to be the most robust antibody for the detection of CD5 achieving a pass rate of 95%?(177/187) with 81% optimal across all formats and products based on that clone. Protocols based on the mAb clone 4C7 was challenged by low analytical sensitivity and 50% of all insufficient results were caused by less successful performance of this clone either as concentrated format or RTU system from Dako/Agilent.
CD138: 386 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 86% (60% optimal). The two widely used mAb clones MI15 and B-A38 provided optimal results on all the main fully automated IHC platforms both as concentrated format and corresponding RTU systems. A 100% pass rate was observed for the Leica Biosystems and Dako/Agilent RTU systems based on the mAb clone MI15 when applied in compliance with vendor recommended protocol settings.
CK8/18: 282 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 85% (65% optimal) being at the highest level in the nine NordiQC assessments performed. The extended use of highly sensitive and robust antibodies as the clone cocktails B22.1/B23.1 and EP17/30 on the expense of the less successful clone DC10 has been a main contributor for the improved pass rate. In addition, the identification of liver as a reliable critical tissue control to evaluate a successful IHC assay for CK8/18 in the diagnostic work-up for CUP has been instrumental for the improvement.
EpCAM: A record high number of 345 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 48% (15% optimal). As seen in previous assessments for EpCAM, the selection of antibody must be made with focus on the IHC platform and reagents available in the laboratory. The most commonly used mAb clone Ber-EP4 requires HIER in a special formulated buffer available for the Dako/Agilent IHC platforms and here provides high pass rates both within LD assays or as RTU system for Dako Omnis. On e.g. the Ventana BenchMark IHC platforms, mAb clones BS14 and VU-1D9 had significantly higher pass rates compared to mAb clones Ber-EP4 and MOC-31.
PSA: 377 laboratories participated and a pass rate of 85% was observed (50% optimal). As concentrated format within a laboratory developed test, mAb clone 35H9 and rmAb EP109 were most successful, whereas the mAb clone ER-PR8 proved to be more challenging and needed a carefully calibration of both antibody titer and choice of detection system. The RTU systems from Ventana/Roche and Leica Biosystems based on a pAb and mAb clone 35H9, respectively were very successful providing a high proportion of sufficient and optimal results.
Breast module - run B36
Estrogen receptor (ER): 440 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 78% being reduced compared to the levels obtained in the latest assessments. Too weak or false negative staining reactions were the predominant features of insufficient results. The widely used rmAb clones SP1 and EP1 and mAb clone 6F11 could all be used to provide an optimal result. 91% of the participants used RTU systems for the demonstration of ER. The RTU system from Dako/Agilent based on clone EP1 for Omnis was most successful providing a pass rate of 91%. Tonsil was found to be recommendable as positive and negative tissue control.
HER2 IHC: 419 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 86% (53% optimal) being slightly reduced compared to run B35 but on par to the level observed in runs B33 and B34. In this assessment, the well-established CE-IVD approved HER2 IHC assays PATHWAY® and HER2 4B5, Ventana/Roche, but also the recently launched 2’ generation HercepTest™ Dako/Agilent for Omnis were most successful providing a pass rate of 93%-94%. The “classical” Dako/Agilent HercepTest™ for Autostainer gave a disappointing pass rate of 38%. LD assays based on a concentrate or RTU with no predictive claim were used by 20% of participants giving a pass rate of 72% (28% optimal). The insufficient results were primarily caused by false negative results, whereas a minor proportion caused by poor signal-to-noise ratio compromising the read-out or false positive results.
Companion module - run C14
PD-L1 TPS/CPS (KEYTRUDA®): 243 laboratories participated and an unexpected and relatively low pass rate of 69% was obtained being significantly reduced compared to the latest runs. The PD-L1 IHC pharmDx assay, 22C3 GE006, Dako/Agilent applied in concordance to the vendor recommended guidelines, was most successful providing a pass rate of 100%, 90% optimal. Surprisingly and as yet unexplained due to unknown reasons, the Ventana/Roche PD-L1 IHC assays 741-4905 and 740-4907 for BenchMark (Ultra Plus/Ultra/XT/GX) based on the rmAb clone SP263 provided an overall low pass rate of 40% being inferior to the level expected and obtained in previous runs. LD assays based on concentrated formats and RTU systems without predictive claims provided a pass rate of 76%.
PD-L1 IC score (TECENTRIQ®): 129 laboratories participated and a low pass rate of 56% was observed being reduced from the level of 68% obtained in run C13. The two PD-L1 SP142 CDx IHC assays product no. 741-4860 and 790-4860, Ventana/Roche were as seen previously the most successful assays providing a pass rate of 66% and 67%, respectively but reduced from recent levels. PD-L1 CDx assays as SP263 (741-4905, Ventana/Roche) and 22C3 (SK006/GE006, Dako/Agilent) being successful in the PD-L1 TPS/CPS assessments provided only few sufficient results. Insufficient results were characterized by either pure false negative results (seen for SP142) or false positive results often combined with extensive reaction in tumour cells in the carcinomas compromising the scoring of PD-L1 in immune cells (non-SP142 based assays).
HER2 ISH module - run H24
HER2 ISH: 176 laboratories participated in the technical assessment of HER2 ISH (BRISH) and obtained a pass rate of 79% (36% optimal). The improvement was primarily related to the changed assessment criteria, allowing large negative areas of >25% providing the individual tissue cores still could be evaluated with confidence. The VENTANA HER2 Dual ISH DNA Probe Cocktail, 800-6043 was used by 89% of the participants either as single assay or in combination with HER2 IHC. The insufficient results were typically characterized by large negative areas in one or more of the breast carcinoma samples compromising the evaluation of HER2 gene status, but also caused by impaired morphology, generally weak or missing signals.
225 laboratories participated in the HER2 ISH scoring module and the consensus rate was 94%, and 76% for laboratories using FISH and BRISH, respectively.
December 11th 2023
Søren Nielsen
Scheme director

Run 68 (General module) and C13 (Companion module) were accomplished April to July 2023.
As usual, a short summary of the results is given below. Click on the epitope name to see the complete and detailed assessment report for the individual markers evaluated. In each assessment report, NordiQC intended to identify best practice methods and recommendable immunohistochemical critical assay performance controls (iCAPCs) to both guide the IHC protocol set-up and to monitor the IHC performance within the laboratories.
As specified previously, we do encourage participants to update the submitted protocol settings and reagents used if changed from initial data of entry. Protocols can be updated until the slide return deadline. The submitted data are used to analyze the overall performance and identify root causes for both inferior and optimal performance.
Due to the relatively low pass rate and being a new IHC test, PRAME will be repeated in 2024 and reassessment will not be available.
General module - run 68
CD10: 403 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 73% (48% optimal) being a slight improvement compared to the recent run 66. The widely used mAb clone 56C6 provided an optimal result on all the main fully automated IHC platforms both as concentrated format and corresponding RTU systems. The recently launched RTU system from Dako/Agilent based on mAb clone DAK-CD10 for Dako Omnis was most successful both when used by vendor recommended or modified protocol settings. As seen in run 66, the Ventana/Roche RTU system based on rmAb clone SP67 being applied by 33% of all participants showed an inferior performance.
MSH2: 350 laboratories participated and obtained a relatively high pass rate of 91% (62% optimal). This was the fifth NordiQC assessment of MSH2 and a consistent improved performance has been observed since 2014. The extended use and access to high quality IHC RTU systems from the main IHC vendors have impacted positively to the pass rate. In total 88% of the participants used RTU systems. Especially the RTU systems for fully automated IHC systems from the three main providers (Dako/Agilent, Leica Biosystems and Ventana/Roche) were successful, providing a pass rate of 100%, compared to 73% for laboratory developed assays based on concentrates.
PAX8: 368 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 54% (32% optimal). The pass rate has now improved slightly but at a slow pace from the low level of 37% in run 56, 2019. In concordance to the previous assessments especially the rmAbs clone SP348 but also QR016 were most successful. In contrast, the widely used mAb clone MRQ-50 provided a poor performance especially on the Ventana BenchMark and Dako Omnis platforms giving a too low analytical sensitivity and at the same time it also gave a cross-reaction to other PAX subtypes as PAX5 in B-cells. The contrast in performance for SP348 versus MRQ-50 was in this assessment quite remarkable; irrespective of protocol settings applied, SP348 gave a pass rate of 91% compared to 50% for MRQ-50.
PRAME: 222 laboratories participated in this first assessment of PRAME and obtained a pass rate of 73% (38% optimal). The assessment focused on PRAME being used in the diagnostic work-up in the differential diagnosis between malignant melanoma and benign melanocytic lesions. The most cited and in this assessment widely used rmAb clone EPR20330 proved to be most robust with a pass rate of 80%, 47% optimal and provided optimal results on all the main automated IHC platforms (Dako/Agilent, Leica Biosystems and Ventana/Roche). Both false negative and false positive results were observed. Due to the relatively low pass rate and being a new IHC test, PRAME will be repeated in 2024 and reassessment will not be available.
TTF1: 401 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 81% (71% optimal) being the all-time highest level in the eight assessment runs performed by NordiQC. In concordance with previous NordiQC assessments for TTF1, the mAb clone SPT24 and the rmAb clone SP141 were most reliable for the demonstration of TTF1 providing pass rates of 97% and 96%, respectively. In contrast, mAb clone 8G7G3/1 was less successful and provided a significantly lower pass rate of 6%. Too weak or false negative staining reactions were seen in 87% of the insufficient results.
URO II/III: 107 laboratories participated in this second assessment of URO II/III and obtained a pass rate of 49% (29% optimal). As observed in the first run, antibodies targeted for URO II were most successful. The concentrated format of mAb clone BC21, within a laboratory developed assay, provided the highest proportion of optimal results, 41%, being observed on all main fully automated IHC platforms.
Companion module - run C13
PD-L1 TPS/CPS: 243 laboratories participated being the highest level till now and a very satisfactory pass rate of 92% was observed. This NordiQC assessment for PD-L1 focused on TPS and CPS status in NSCLC and TNBC, respectively. Similar to observations seen in previous runs, the insufficient PD-L1 IHC results were most frequently characterized by a too low TPS/CPS level changing PD-L1 status in one or more of the carcinomas included. The PD-L1 IHC pharmDx assay, 22C3 GE006, Dako/Agilent applied in concordance to the vendor recommended guidelines, was most successful providing a pass rate of 100%, with an optimal rate of 79%.
PD-L1 IC score: 139 laboratories participated and a relatively low pass rate of 68% was observed, however slightly increased compared to the levels seen in the latest runs. The assessment for PD-L1 IC score focused on the evaluation of the analytical accuracy of the PD-L1 IHC assays for urothelial carcinomas and TNBCs. The insufficient results were characterized by either pure false negative results (seen for SP142 based assays), false positive results (seen for non-SP142 based assays) or an extensive staining reaction in tumour cells compromising the evaluation of PD-L1 reaction in immune cell. In concordance with previous runs, the Ventana/Roche PD-L1 SP142 IHC assay 741-4860 was most successful providing a pass rate of 82%.
July 10th 2023
Søren Nielsen
Scheme director
Run 67 (General module), B35 (breast module) and H23 were accomplished from January to April 2023. In total, about 500 laboratories participated in at least one of the modules offered, and more than 3.200 slides were assessed.
As usual, a short summary of the results is given below. Click on the epitope name to see the complete and detailed assessment report for the individual markers evaluated. In each assessment report, NordiQC intended to identify best practice methods and recommendable immunohistochemical critical assay performance controls (iCAPCs) to both guide the IHC protocol set-up and to monitor the IHC performance within the laboratories.
As specified previously, we do encourage participants to update the submitted protocol settings and reagents used if changed from initial data of entry. The submitted data are used to analyze the overall performance and identify root causes for both inferior and optimal performance.
Due to the relatively low pass rates for CGA and p53, these will be repeated in 2024 and reassessment will not be available.
General module - run 67
CD4: 332 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 80% (61% optimal). The rmAb clone SP35 was most successful providing an optimal result on all the main fully automated IHC platforms both as concentrated format and especially as corresponding RTU system from Ventana/Roche with a pass rate of 98%. The mAb clone 4B12 was widely used both as concentrate and within RTU systems but showed inferior performance on fully automated platforms especially on Dako Omnis. The Dako/Agilent RTU format IS/IR649 for Autostainer based on clone 4B12 was frequently migrated to Dako Omnis (n=28) with an unacceptable pass rate of 0%.
CGA: 365 laboratories participated and obtained a relatively low pass rate of 64% (32% optimal). This was the eigth NordiQC assessment of CGA. A reduced pass rate was observed compared to the previous runs, which mainly was due to less robust Abs as mAb clones DAK-A3 and 5H7 being used by 16% of all participants with a low pass rate of 5%, none optimal. In contrary mAb clone LK2H10 was very successful and in particular as RTU from Ventana/Roche. In concordance with previous assessments for CGA, appendix was found recommendable as positive and negative tissue control. Due to the relatively low pass rate, CGA will be repeated in 2024, run 68 and reassessment will not be available.
MLH1: 342 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 71% (46% optimal). Several Abs could be used for an optimal result. Irrespective of the Ab applied, sufficient HIER, use of a highly sensitive detection system and careful calibration of the primary antibody were the most important prerequisites for an optimal staining result. Overall, the mAb clone ES05 (both concentrate and as RTU) applied on the Leica Bond stainer platforms provided the highest pass rate of 94%, 82% optimal when used with an alkaline HIER buffer and a 3-step detection system.
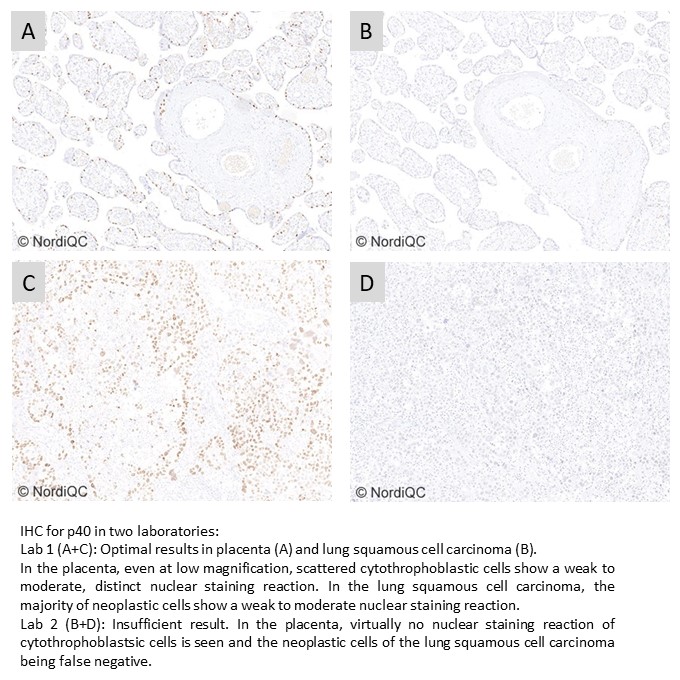
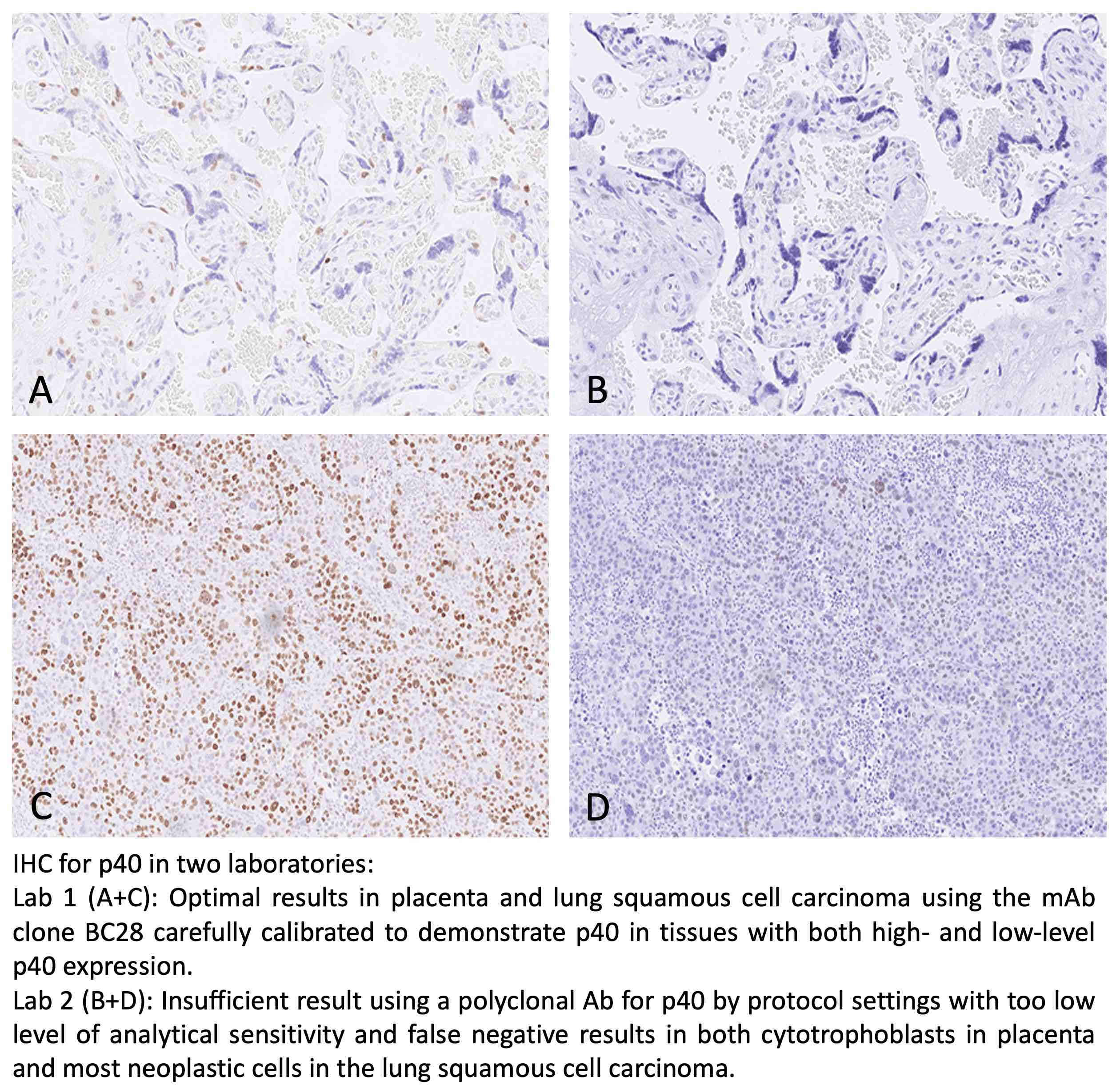
p40: 343 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 85% (60% optimal). The assessment focused on p40 being used in the diagnostic work-up in in the differential diagnosis between lung squamous cell carcinoma and lung adenocarcinoma. This was the fourth assessment of p40 in NordiQC and increased and stabile pass rate has been obtained compared to the initial runs. The extended use of the highly sensitive and robust mAb clone BC28 both as concentrate and as RTU format on the expense of pAbs has been instrumental for the improvement. Additionally, the recently launched RTU system from Dako/Agilent based on mAb clone DAK-p40 giving a pass rate of 100% impacted positively on the overall pass rate.
p53: 372 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 65% (29% optimal) being an improvement from 44% and 55% in run 63 and 55, respectively but still significantly inferior the level of 79% in run 38, 2013. Similar to the two previous runs, this assessment focused on IHC for p53 to demonstrate different TP53 mutations in endometrial carcinomas. The widely used mAbs clones BP53-11 and DO-7 could both be used to provide optimal results providing the protocols were based on efficient HIER in an alkaline buffer and of central importance in combination with a 3-step detection system. As a consequence of the “new purpose of p53 IHC” the most important parameter being a careful calibration of the primary Ab to consistently identify p53 in low-level expressing structures as dispersed normal lymphocytes and stromal cells being of central importance in the diagnosis of carcinomas with loss of p53 expression. Due to the relatively low pass rate, p53 will be repeated in 2024 and reassessment will not be available.
Breast module - run B35
Estrogen receptor (ER): 422 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 91% (58% optimal). The widely used rmAb clones SP1 and EP1 and mAb clone 6F11 could all be used to provide an optimal result. 89% of the participants used RTU systems for the demonstration of ER. The RTU systems from Ventana/Roche based on clone SP1 for BenchMark and Dako/Agilent based on EP1 for Omnis were most successful providing a pass rate of 100% and 98%, respectively. Too weak or false negative staining reactions were the predominant features of insufficient results, but in a few cases false positive results were observed (mAb clone 6F11). Tonsil was found to be recommendable as positive and negative tissue control.
Progesterone receptor (PR): 414 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 92% (60% optimal) being virtual identical to the level seen in the last four runs. mAb clones 16, PgR 636, PgR 1294 and rmAb clone 1E2 could all be used to provide an optimal result. 84% of the participants used RTU systems from Ventana/Roche, Dako/Agilent and Leica Biosystems and in total obtained a pass rate of 95% when applying these assays as “plug-and-play”. The Leica Biosystems’ RTU system based on clone 16 was most successful with 100% optimal results. In this assessment, too weak or false negative staining reactions were the predominant features of insufficient results. Tonsil and uterine cervix in combination are recommendable negative and positive tissue controls.
HER2 IHC: 403 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 90% (66% optimal). In this assessment, the CE-IVD approved HER2 IHC assay PATHWAY®, Ventana/Roche, VENTANA HER2 4B5 and the recently launched HercepTest™ Dako/Agilent for Omnis were most successful providing a pass rate of 95%, 94% and 100%, respectively. LD assays based on a concentrate or RTU with no predictive claim were used by 20% of participants giving an overall pass rate of 79%. The insufficient results were primarily characterized by reduced proportion of positive cells, a too weak or false negative staining reaction
HER2 ISH module - run H23
HER2 ISH: 163 laboratories participated in the technical assessment of HER2 ISH (BRISH) and obtained a pass rate of 59% (37% optimal) and slightly reduced compared to run H22. The VENTANA HER2 Dual ISH DNA Probe Cocktail, 800-6043 was used by 90% of the participants either as single assay or in combination with HER2 IHC. As observed in virtually all latest assessments, the insufficient results were mainly caused by large negative areas and missing signals in >25% of the neoplastic cells in one or more of the samples included.
207 laboratories participated in the HER2 ISH scoring module (65 via FISH and 142 via BRISH) and the consensus rate was 98%, and 80% for laboratories using FISH and BRISH, respectively.
April 26th 2023
Søren Nielsen
Scheme director
Run 66 (General module), B34 (Breast module), C12 (Companion module) and H22 (HER2 ISH module) were accomplished from October to December 2022. In total, about 500 laboratories participated in at least one of the modules offered, and more than 2.900 slides were assessed.
As usual, a short summary of the results is given below. Click on the epitope name to see the complete and detailed assessment report for the individual markers evaluated. In each assessment report, NordiQC intended to identify best practice methods and recommendable immunohistochemical critical assay performance controls (iCAPCs) to both guide the IHC protocol set-up and to monitor the IHC performance within the laboratories.
As specified previously, we do encourage participants to update the submitted protocol settings and reagents used if changed from initial data of entry. The submitted data are used to analyze the overall performance and identify root causes for both inferior and optimal performance.
Please be aware that we now have opened for protocol submission for the Winter run: General module run 67, Breast module run B35 and HER2 ISH module H23.
General module - run 66
BSAP: 259 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 86% (52% optimal). Several antibody clones could be used to obtain an optimal result. The mAb clone DAK-Pax5 was found very robust and the RTU systems from Dako/Agilent based on this clone (IR650 and GA650) provided superior results, when applied by the vendor recommended settings. Protocols based on the mAb clones 1EW, 24 and the rmAb clone SP34 were often challenged by low analytical sensitivity and/or poor signal-to-noise ratio hindering interpretation of the specific signal for BSAP.
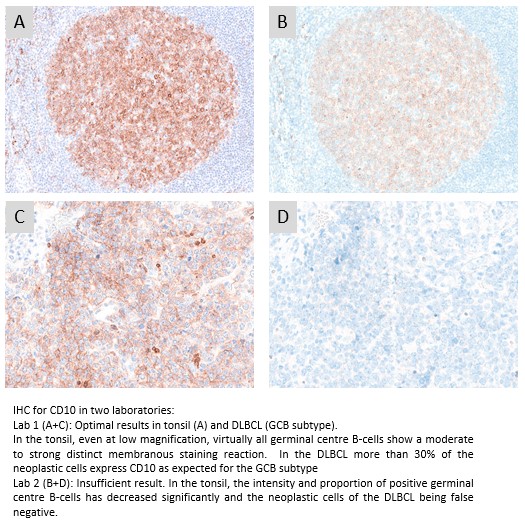
CD10: 393 laboratories participated and obtained a relatively low pass rate of 64% (37% optimal). The widely used mAb clone 56C6 provided an optimal result on all the main fully automated IHC platforms both as concentrated format and corresponding RTU systems. The Leica Biosystem RTU system based on mAb clone 56C6 gave a pass rate of 100%, when used by recommended protocol settings. The recently launched RTU system from Dako/Agilent based on mAb clone DAK-CD10 was also very successful, whereas the Ventana/Roche RTU system using rmAb clone SP67 being applied by 32% of all participants showed an inferior performance. Due to the relatively low pass rate, CD10 will be repeated in 2023, run 68 and reassessment will not be available.
Napsin A: 321 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 83% (46% optimal). The pass-rate has improved consistently in the three assessments conducted in NordiQC and mainly related to the extended use of robust and specific monoclonal primary Abs as the clones IP64 and MRQ-60 on the expense on polyclonal Abs typically giving aberrant and false positive results.
SMH: 152 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 81% (58% optimal). The assessment focused on SMH being used in the diagnostic work-up in breast samples to distinguish benign and precursor lesions from invasive cancer. The widely used mAb clone SMMS-1 provided an optimal result on all the main fully automated IHC platforms both as concentrated format and corresponding RTU systems. The Dako/Agilent RTU format IS/IR066 for Autostainer based on clone SMMS-1 was frequently migrated to Dako Omnis with an inferior result giving an unacceptable pass rate of 15%.
SYP: 390 laboratories participated and a pass rate of 70% was observed (47% optimal). This was the seventh NordiQC assessment of SYP. A reduced pass rate was observed compared to the two previous runs, which primarily was due to extended use of RTU systems with less successful vendor recommended protocol settings, off-label use of RTU formats and less robust Abs in general. Duodenum seemed to be a recommendable positive tissue control for SYP using goblet cells as iCAPC for analytical sensitivity.
Breast module - run B34
Estrogen receptor (ER): 406 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 93% (63% optimal). The widely used rmAb clones SP1 and EP1 and mAb clone 6F11 could all be used to provide an optimal result. 89% of the participants used RTU systems for the demonstration of ER. The RTU systems from Ventana/Roche based on clone SP1 for BenchMark and Dako/Agilent based on EP1 for Omnis were most successful providing a pass rate of 94% and 97%, respectively. Too weak or false negative staining reactions were the predominant features of insufficient results. Tonsil was found to be recommendable as positive and negative tissue control.
HER2 IHC: 392 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 84% (70% optimal). In this assessment, the CE-IVD approved HER2 IHC assay PATHWAY®, Ventana/Roche and the recently launched HercepTest™ Dako/Agilent for Omnis were most successful providing a pass rate of 93% and 100%, respectively. The “classical” Dako/Agilent HercepTest™ for Autostainer gave a disappointing pass rate of 33%. LD assays based on a concentrate or RTU with no predictive claim were used by 21% of participants giving a pass rate of 77% (56% optimal). The insufficient results were primarily caused by false negative results or poor signal-to-noise ratio compromising the read-out.
Companion module - run C12
PD-L1 TPS/CPS (KEYTRUDA®): 232 laboratories participated and a pass rate of 85% was observed. This was the second NordiQC assessment of PD-L1 for TPS/CPS status with focus on TNBCs in addition to NSCLCs. Similar to observations seen in previous runs, the insufficient PD-L1 IHC results were most frequently characterized by a too low TPS/CPS level changing PD-L1 status in one or more of the carcinomas included. The PD-L1 IHC pharmDx assay, 22C3 GE006, Dako/Agilent applied in concordance to the vendor recommended guidelines, was most successful providing a pass rate of 100%, with an optimal rate of 79%, being superior to the other companion diagnostic assays and LD assays based on concentrated Abs or RTU systems without predictive claim.
PD-L1 IC score (TECENTRIQ®): 134 laboratories participated and a relatively low pass rate of 64% was observed – slightly increased compared to the level seen in run C11. The assessment for PD-L1 IC score focused on the evaluation of the analytical accuracy of the PD-L1 IHC assays for urothelial carcinomas and TNBCs. The insufficient results were characterized by either pure false negative results (seen for SP142 based assays) or an extensive staining reaction in tumour compromising the evaluation of PD-L1 reaction in immune cells in combination with an either false negative or false positive result (seen for non-SP142 based assays). In concordance with previous runs, the Ventana/Roche PD-L1 SP142 IHC assay 741-4860 was most successful providing a pass rate of 87%.
HER2 ISH module - run H22
HER2 ISH: 165 laboratories participated in the technical assessment of HER2 ISH (BRISH) and obtained a pass rate of 64% (32% optimal) and slightly improved compared to run H21. The VENTANA HER2 Dual ISH DNA Probe Cocktail, 800-6043 was used by 80% of the participants giving a pass rate of 68%. As observed in virtually all latest assessments, the insufficient results were mainly caused by large negative areas and missing signals in >25% of the neoplastic cells in one or more of the samples included.
207 laboratories participated in the HER2 ISH scoring module (59 via FISH and 148 via BRISH) and the consensus rate was 90%, and 66% for laboratories using FISH and BRISH, respectively.
December 16th 2022
Søren Nielsen
Scheme director

NordiQC has gained accreditation status by DANAK for proficiency testing.
The general, breast cancer and companion modules are accredited per 28.11.2022 by DANAK under registration number 616 to proficiency testing according to ISO 17043. NordiQC is affiliated to and based at Department of Pathology, Aalborg University Hospital, Denmark and in 2020 the department was accredited according to ISO 15189 (Medical laboratories – Requirements for quality and competence).
Run 65 (General module) and C11 (Companion module) were accomplished from March to July 2022. In total, 429 laboratories participated in one or both of the modules offered, and more than 2.200 slides and 12.000 individual tissue cores were assessed.
As usual, a short summary of the results is given below. Click on the epitope name to see the complete and detailed assessment report for the individual markers evaluated. In each assessment report, NordiQC intended to identify best practice methods and recommendable immunohistochemical critical assay performance controls (iCAPCs) to both guide the IHC protocol set-up and to monitor the IHC performance within the laboratories.
As specified previously, we do encourage participants to update the submitted protocol settings and reagents used if changed from initial data of entry. The submitted data are used to analyze the overall performance and identify root causes for both inferior and optimal performance.
Please be aware that we now have opened for protocol submission for the Autumn run: General module run 66, Breast module run B34, Companion module run C12 and HER2 ISH module H22.
General module - run 65
ALK (lung): 256 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 77% (59% optimal). The mAb clones 5A4, OTI1A4 and rmAb clone D5F3 could all both as concentrated format in a LD assay and within a RTU system provide an optimal result. The recently launched RTU system from Dako/Agilent based on OTI1A4 and well-established system from Ventana/Roche based on D5F3 were most successful giving a pass rate of 100% and 95%, respectively. The mAb clone ALK1 was used by 8% of the participants with a pass rate 5%. A sufficient result in ALCL was seen but insufficient/false negative in the lung cancer emphasizing the need to re-optimize IHC protocols for ALK gene rearrangements in lung cancer
AMACR (p504s): 334 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 93% (74% optimal) being on par to the level seen in all four NordiQC runs conducted for AMACR. Virtually identical pass rates were seen for LD assays typically based on the rmAb clone 13H4 and RTU systems based on either rmAb clone 13H4 or SP116. Efficient HIER preferable in an alkaline buffer and careful calibration of the primary Ab were the two main prerequisites for an optimal staining result.
BAP1: 163 laboratories participated in this first assessment of BAP1 and obtained a pass rate of 69% (42% optimal). The focus for BAP1 as marker to differentiate reactive mesothelial lesions from malignant mesothelioma. At present no RTU systems available and all participants applied as such a laboratory developed (LD) assay. The mAb clone C-4 was most widely used and provided an optimal performance all main fully automated IHC platforms. 3-step detections systems were found to be main prerequisite for an optimal result.
CD30: 365 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 75% (44% optimal). The well-established mAb clones Ber-H2 and JCM182 were used by 98% of all participants and applied as RTU systems in 70%. The mAb clone Ber-H2 was found to be most successful when applied in combination with a modified citric based low pH buffer and a 3-step detection system. The mAb clone JCM182 was also successful, but found challenging to calibrate for an optimal result due to an extended reaction in macrophages hampering the selective demonstration of e.g. Hodgkin cells.
CK5: 311 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 71% (44% optimal). The pass rate was improved compared to 58% and 44% observed in the two latest assessments of CK5. As seen previously, the widely used mAb clone XM26 was significantly more successful compared to mAb clone D5/16 B4 with pass rates of 93% and 49%, respectively (pooled data for both concentrated and RTU formats). The mAb clone D5/16 B4 typically provided a too low analytical sensitivity. The RTU system from Ventana/Roche based on rmAb clone SP27 provided an impressive pass rate of 100%, 100% optimal. The improved pass rate in part contributed by harmonization of best practice protocol settings concerning clones, titers if concentrate and use of 3-step detection systems.
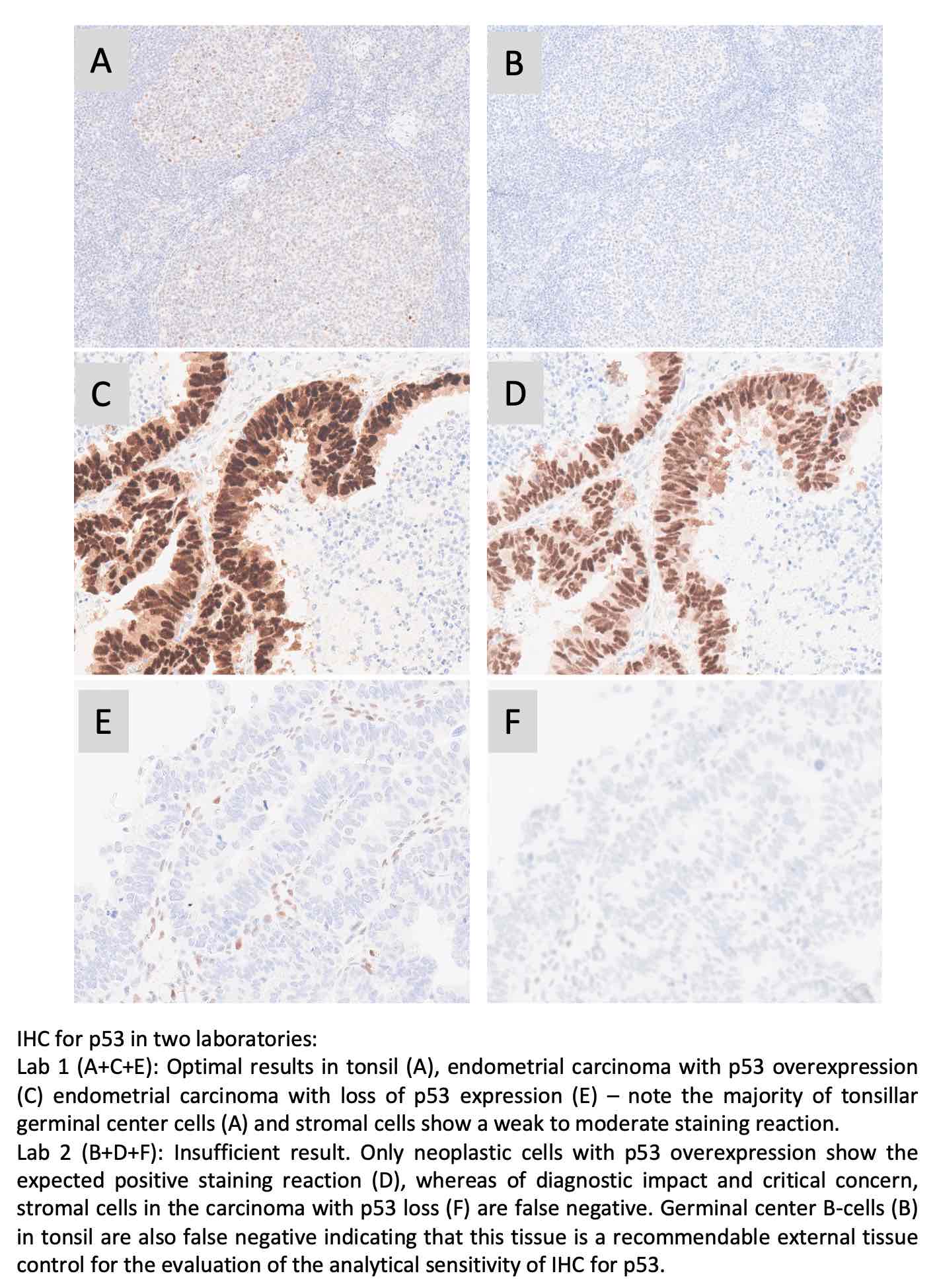
p53: 370 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 55% (23% optimal) being an improvement from 44% in run 63 but still significantly inferior the level of 79% in run 38, 2013. This assessment focused on IHC for p53 to demonstrate different TP53 mutations in endometrial carcinomas. The widely used mAbs clones BP53-11 and DO-7 could both be used to provide optimal results providing the protocols were based on efficient HIER in an alkaline buffer and of central importance in combination with a 3-step detection system. As a consequence of the “new purpose of p53 IHC” the most important parameter being a careful calibration of the primary Ab to consistently identify p53 in low-level expressing structures as dispersed normal lymphocytes and stromal cells being of central importance in the diagnosis of carcinomas with loss of p53 expression. Due to the relatively low pass rate, p53 will be repeated in 2023, run 67 and reassessment will not be available.
Companion module - run C11
PD-L1 (TPS/CPS): 225 laboratories participated and a pass rate of 81% was observed. This was the first NordiQC assessment of PD-L1 for TPS/CPS status with focus on TNBCs in addition to NSCLCs. Similar to observations seen in previous runs, the insufficient PD-L1 IHC results were most frequently characterized by a too low TPS/CPS level changing PD-L1 status in one or more of the carcinomas included. The companion diagnostic PD-L1 IHC assay, 22C3 GE006, Dako/Agilent performed in concordance to the product guidelines, was most successful providing a pass rate of 97%. LD assays based on mAb clone 22C3 and performed on the fully automated platforms BenchMark and Omnis provided highly reproducible results with “an all-time high” pass rate of 95%.
PD-L1 (IC score): 141 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 59%, being on par to run C10 and slightly reduced compared to the results in run C9. The assessment for PD-L1 IC score focused on the evaluation of the analytical accuracy of the PD-L1 IHC assays for urothelial carcinomas and TNBCs. The insufficient results were characterized by either pure false negative results (seen for SP142 based assays) or an extensive staining reaction in tumour compromising the evaluation of PD-L1 reaction in immune cells in combination with an either false negative or false positive result (seen for non-SP142 based assays). In concordance with previous runs, the Ventana/Roche PD-L1 SP142 IHC assays 741-4860 and 790-4860 were most successful providing a pass rate of 79% and 81%, respectively.
July 11th 2022
Søren Nielsen
Scheme director
Run 64 (General module), B33 (Breast module) and H21 (HER2 ISH module) were accomplished from January to April 2021. In total, 517 laboratories participated in one or more of the three modules offered and more than 3.000 slides were assessed.
As usual, a short summary of the results is given below. Click on the epitope name to see the complete and detailed assessment report for the individual markers evaluated. In each assessment report, NordiQC intended to identify best practice methods and recommendable immunohistochemical critical assay performance controls (iCAPCs) to both guide the IHC protocol set-up and to monitor the IHC performance within the laboratories.
We encourage participants to update the submitted protocol settings and reagents used if changed after initial data entry. The data, including lot numbers, are used to analyze the overall performance and identify root causes for both inferior and optimal performance.
General module - run 64
CD56: 364 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 72% (47% optimal). The pass rate increased slightly from the recent assessment run 61, 2021. Similar to all assessments for CD56, the take-home messages being usage of basic highly sensitive protocol settings and of utmost importance selection of a clone either as concentrate or RTU format capable to provide the expected results on the IHC platform used within in the laboratory.
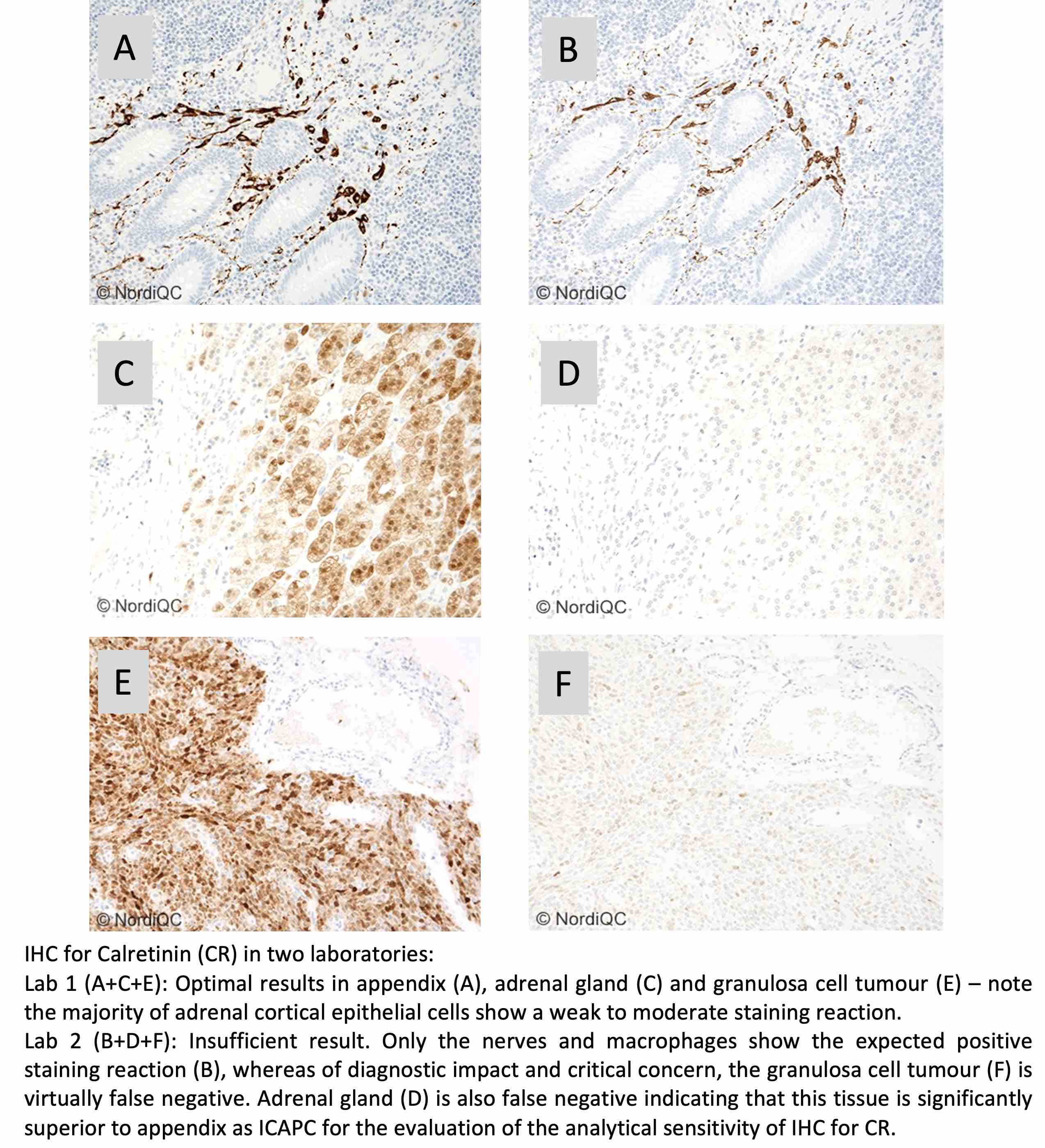
CR: 339 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 76% (50% optimal). In total eleven different Abs/clones could provide an optimal result. 80% of the participants used RTU formats. The Leica Biosystems RTU system based on clone CAL6 most successful followed by the Ventana/Roche system based on rmAb clone SP65. As concentrated format the mAb clone CAL6 provided superior performance and higher proportion of optimal results compared to the mAb clone DAK-Calret1, as the latter being inferior on fully automated systems as Dako Omnis and Ventana BenchMark.
DES: 370 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 69% (41% optimal). The well-established and widely used mAb clones D33 and DE-R-11 were both very successful, providing being applied by appropriate protocol conditions. For mAb clone DE-R-11 application of HIER was found to be the main prerequisite for an optimal result being in contrast to the package insert for the Ventana/Roche RTU system recommending proteolysis providing a disappointing pass rate of 22%, none optimal. The Dako/Agilent RTU format IS/IR606 for Autostainer based on clone D33 was frequently migrated to Dako Omnis with an inferior result and also with an unacceptable pass rate of 22%.
PAX8: 337 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 52% (27% optimal). The pass rate has now improved slightly from the low level of 37% in run 56, 2019. In concordance to the previous assessments the rmAbs clones SP348, ZR-1 and mAb clone BC12 gave encouraging results. In contrast, the widely used mAb clone MRQ-50 provided a poor performance especially on the Ventana BenchMark and Dako Omnis platforms giving a too low analytical sensitivity and at the same time it also gave a cross-reaction to other PAX subtypes as PAX5 in B-cells. Due to the relatively low pass rate, PAX8 will be repeated in 2023 and reassessment will not be available.
SATB2: 173 laboratories participated in this second assessment of SATB2 and obtained a pass rate of 75% (42% optimal) being an improvement from 58% in run 58, 2020. The majority of participants used the rmAb clone EP281 and was found to be more successful compared to other Abs as e.g., mAb clone SATBA4B10 and pAbs. Used within a LD assay, optimal results of EP281 could be obtained on all main fully automated IHC platforms especially when applied with HIER in an alkaline buffer and a 3-step detection system. LD assays and RTU formats/systems of EP281 provided similar performance.
Breast module - run B33
Estrogen receptor (ER): 407 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 89% (54% optimal) being identical to the level seen in B32. rmAb clones SP1 and EP1 and mAb clone 6F11 could all be used to provide an optimal result. 86% of the participants used RTU systems for the demonstration of ER and provided an overall pass rate of 91%. The RTU systems from Ventana/Roche based on clone SP1 and Dako/Agilent clone EP1 (Omnis), were most successful with pass rates of 96% and 97%, respectively, when used by vendor recommended protocol settings. Too weak or false negative staining reactions were the predominant features of insufficient results. Tonsil was found to be recommendable as positive and negative tissue control.
Progesterone receptor (PR): 404 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 91% (61% optimal) being on par to the level seen in the last three runs. mAb clones 16, PgR 636, PgR 1294 and rmAb clone 1E2 could all be used to provide an optimal result. 78% of the participants used RTU systems from Ventana/Roche, Dako/Agilent and Leica Biosystems and in total obtained a pass rate of 93% when applying these assays as “plug-and-play”. The Leica Biosystems’ RTU system based on clone 16 was most successful with 100% optimal results. In this assessment, a false negative staining reaction was the predominant feature of the insufficient results, but false positive results were also observed. Tonsil and uterine cervix in combination were found to be recommendable negative and positive tissue controls.
HER2 IHC: 384 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 82% (54% optimal) almost identical to the latest run B32 and slightly reduced compared to the level seen in the three previous assessment runs B29-B31. In this assessment, the CE-IVD approved HER2 IHC assay PATHWAY®, Ventana/Roche and the recently launched HercepTest™ Dako/Agilent for Omnis were most successful providing a pass rate of 93% and 100%, respectively, however PATHWAY® with a higher proportion of optimal results of 79% compared to 35% for HercepTest™, Dako Omnis. LD assays based on a concentrate or RTU with no predictive claim were used by 22% of participants giving a pass rate of 71%. The insufficient results were primarily characterized by false negative results or a poor signal-to-noise ratio compromising the read-out.
HER2 ISH module - run H21
HER2 ISH: 154 laboratories participated in the technical assessment of HER2 ISH (BRISH) and obtained a pass rate of 56% (45% optimal) and the level declined in most recent assessments. The VENTANA HER2 Dual ISH DNA Probe Cocktail, 800-6043 and INFORM™ HER2 Dual ISH assay, 780-4422/800-4422 were used by 93% of all participants. As observed in virtually all latest assessments, the insufficient results were mainly caused by large negative areas and missing signals in >25% of the neoplastic cells in one or more of the samples included.
204 laboratories participated in the HER2 ISH scoring module (65 via FISH and 139 via BRISH) and, the consensus rate was 85%, and 86% for laboratories using FISH and BRISH, respectively.
April 22th 2022
Søren Nielsen,
Scheme director

Run 63 (General module), B32 (Breast module), C10 (Companion modules) and H20 (HER2 ISH module) were accomplished from September to December 2021. In total, 535 laboratories participated in one or more of the modules offered and more than 3.000 slides were assessed.
Please note, due to low pass rates of CK5 and p53, these will be repeated in run 65, 2022. Therefore no reassessment of these two markers will be available.
As usual, a short summary of the results is given below. Click on the epitope name to see the complete and detailed assessment report for the individual markers evaluated. In each assessment report, NordiQC intended to identify best practice methods and recommendable immunohistochemical critical assay performance controls (iCAPCs) to both guide the IHC protocol set-up and to monitor the IHC performance within the laboratories.
General module - run 63
CD3: 355 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 95% (71% optimal). The very high and encouraging pass rate has increased since the last assessment of CD3 and the access to both several high quality concentrated formats of CD3 antibodies providing optimal results on all main IHC platforms and the wide usage of corresponding optimally calibrated RTU systems seem to be the main pillars for the improvement.
CD79a: 324 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 89% (65% optimal). The well-established and widely used mAb clone JCB117 and rmAb clone SP18 were both very successful both within a LD assay and especially as RTU systems for the fully automated IHC platforms from Dako/Agilent, Ventana/Roche and Leica Biosystems. HIER in alkaline buffer and use of a 3-step polymer or multimer based detection system were the main prerequisites for an optimal result.
CK5: 283 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 58% (39% optimal). Despite the pass rate was improved compared to 44% observed in that latest assessment of CK5, run 55 2019, the level is still unsatisfactory. The well-established clone D5/16 B4 provided an overall inferior performance characterized by too low analytical sensitivity, whereas the mAb clone XM26 both as concentrated format within a LD assay or as RTU system from Leica Biosystems was significantly more successful. Also, the RTU system from Ventana/Roche based on clone SP27 provided an impressive pass rate of 100%.
GATA3: 320 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 68% (41% optimal). This was the third assessment of GATA3 in NordiQC and focused on the application in the diagnostic work-up of cancers of unknown primary origin. The vast majority of participants used the mAb clone L50-823. Used within a LD assay, optimal results could be obtained on all main fully automated IHC platforms. The Ventana/Roche RTU system based on clone L50-823 gave the highest pass rate and proportion of optimal results.
p53: 351 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 46% (23% optimal) being significantly inferior to the pass rate of 79% in the recent run 38, 2013. The assessment focused on p53 to demonstrate TP53 mutations in endometrial carcinomas. The widely used mAbs clones BP53-11 and DO-7 could both be used to provide optimal results providing the protocols were based on efficient HIER in an alkaline buffer and a 3-step detection system was applied. However, the most important parameter being a careful calibration of the primary Ab to consistently identify p53 in low-level expressing structures as dispersed normal lymphocytes and stromal cells being of central importance in the diagnosis of carcinomas with loss of p53 expression.
Breast module - run B32
Estrogen receptor (ER): 379 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 89% (55% optimal). rmAb clones SP1 and EP1 and mAb clone 6F11 could all be used to provide an optimal result. 88% of the participants used RTU systems for the demonstration of ER. The RTU system from Ventana/Roche based on clone SP1, was most successful with a pass rate of 98% (76% optimal) when used by vendor recommended protocol settings. Too weak or false negative staining reactions were the predominant features of insufficient results. Tonsil was found to be recommendable as positive and negative tissue control.
HER2 IHC: 363 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 82% (54% optimal). In this assessment, the CE-IVD approved HER2 IHC assay PATHWAY®, Ventana/Roche and the recently launched HercepTest™ Dako/Agilent for Omnis were most successful providing a pass rate of 97% and 100%, respectively. The “classical” Dako/Agilent HercepTest™ for Autostainer gave a disappointing pass rate of 57%. LD assays based on a concentrate or RTU with no predictive claim were used by 22% of participants giving a pass rate of 58%. The insufficient results were primarily characterized by false negative results or a poor signal-to-noise ratio compromising the read-out.
HER2 ISH module - run H20
HER2 ISH: 147 laboratories participated in the technical assessment of HER2 ISH (BRISH) and obtained a pass rate of 65% (50% optimal) slightly inferior to the level obtained in most recent assessments. The VENTANA HER2 Dual ISH DNA Probe Cocktail, 800-6043 and INFORM™ HER2 Dual ISH assay, 780-4422/800-4422 were used by 94% of all participants. As observed in virtually all latest assessments, the insufficient results were mainly caused by large negative areas and missing signals in >25% of the neoplastic cells in one or more of the samples included.
Companion module - run C10
PD-L1 TPS/CPS (KEYTRUDA®): 218 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 78% (49% optimal). Similar to observations seen in previous runs, the insufficient PD-L1 IHC results were most frequently characterized by a too low TPS/CPS level changing PD-L1 status in one or more of the carcinomas included. The companion diagnostic PD-L1 IHC assay, 22C3 GE006, Dako/Agilent performed in concordance to the product guidelines, was most successful providing a pass rate and proportion of optimal results of 100%. LD assays were used by 50% of the participants and an inferior pass rate of 50% was observed.
PD-L1 IC (TECENTRIQ®): 159 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 60% (29% optimal), being slightly reduced compared to the results in the recent run C9. The assessment for PD-L1 IC focused on the evaluation of the analytical accuracy of the PD-L1 IHC assays for urothelial carcinomas and TNBCs. Insufficient results were most frequently characterized by a reduced proportion, too weak or false negative staining reaction of immune cells and/or combined with an excessive staining reaction of tumour cells compromising the evaluation of PD-L1 status in the immune cells. In concordance with previous runs, the Ventana/Roche PD-L1 SP142 IHC assays 741-4860 and 790-4860 were most successful providing a pass rate of 78% and 76%, respectively.
December 10th 2021
Søren Nielsen
Scheme director

Run 62 (General module) and C9 (Companion modules) were accomplished from April to July 2021. In total, 416 laboratories participated in one or more of the modules offered and in total more than 2.100 slides were assessed.
As usual, a short summary of the results is given below. Click on the epitope name to see the complete and detailed assessment report for the individual markers evaluated. In each assessment report, NordiQC intended to identify best practice methods and recommendable immunohistochemical critical assay performance controls (iCAPCs) to both guide the IHC protocol set-up and to monitor the IHC performance within the laboratories.
General module - run 62
BRAF: 135 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 72% (35% optimal). This was the first assessment of BRAF in NordiQC and it focused on the demonstration of corresponding BRAF V600E mutations in melanomas and colorectal adenocarcinomas. Optimal staining results could only be obtained with the mAb clone VE1 either applied as concentrated format or RTU system on the Ventana/Roche BenchMark platforms. Optimal results were mainly obtained by using efficient HIER in an alkaline buffer and use of a highly sensitive multimer based detection system with tyramide amplification (OptiView + Amplification).
CD31: 342 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 79% (56% optimal). The assessment focused on the demonstration of CD31 to identify angiosarcomas in the characterization of cancers of unknown origin and tumour cell invasion in vascular structures. The well-established and widely used mAb clone JC70A was most successful both within a LD assay and especially as RTU system from Dako/Agilent and Leica Biosystems. HIER in alkaline buffer or TRS low pH (Dako/Agilent), precise calibration of the primary Ab and use of a 3-step polymer or multimer based detection system were the main prerequisites for an optimal result.
CK7: 359 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 94% (74% optimal). This was the fourth assessment of CK7 in NordiQC and it focused on the application in the diagnostic work-up of cancers of unknown primary origin. The RTU systems IR/GA619 (Dako/Agilent), PA0942/PA0138 (Leica Biosystems) and 790-4462 (Ventana/Roche) based on the clones OV-TL 12/30, RN7 and SP52, respectively, provided superior performance and applying vendor recommended protocol settings, all participants using one of the RTU systems obtained a sufficient result.
CK20: 360 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 94% (74% optimal). This was the fifth assessment of CK20 in NordiQC and it focused on the application in the diagnostic work-up of cancers of unknown primary origin. Similar to CK7, the RTU systems from Dako/Agilent, Leica Biosystems and Ventana/Roche, based on mAb clone Ks20.8 and rmAb clone SP33, respectively, provided the highest proportion of sufficient and optimal results and applying vendor recommended protocol settings, all participants using one of the RTU systems obtained a sufficient result. mAb clone Ks20.8 was the most widely used antibody within laboratory developed tests, and superior performance was obtained if HIER was used for pre-treatment compared to proteolysis.
PAX8: 310 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 45% (19% optimal) and slightly improved the pass rate of 39% in the recent run 60, 2020. The assessment focused on PAX8 used to identify the origin of renal cell and ovarian carcinoma in the diagnostic work-up of cancer of unknown primary origin. The rmAbs clones EP298, ZR-1 and especially SP348 gave encouraging results and a high proportion of sufficient results on the main fully automated platforms. In contrast, the widely used mAb clone MRQ-50 provided a poor performance especially on the Ventana BenchMark and Dako Omnis platforms giving a too low analytical sensitivity and at the same time it also gave a cross-reaction to other PAX subtypes as PAX5 in B-cells. Due to the low pass rate, PAX8 will be repeated in 2022 and reassessment will not be available.
PMS2: 302 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 70% (43% optimal). This was the third NordiQC assessment of PMS2 and a decrease in the pass rate was seen compared to the previous runs. Optimal results were obtained by the rmAb clones EP51 and EPR3947 and mAb clones A16-4 and MRQ-28 using HIER in an alkaline buffer and 3-step detection system. Clone EP51 was found successful on the main fully automated platforms both as concentrate and corresponding RTU system e.g. from Dako/Agilent and Leica Biosystems. In this assessment the recently launched RTU system from Ventana/Roche based on clone A16-4 provided an inferior performance and a pass rate of 49% when used accordingly to the recommended protocol settings.
Companion module - run C9
PD-L1 TPS/CPS (KEYTRUDA®): 211 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 82% (47% optimal). This assessment for PD-L1 TPS/CPS ( KEYTRUDA®) focused on the evaluation of the analytical accuracy of the IHC assays to identify patients with NSCLCs and urothelial carcinomas to be treated with KEYTRUDA® as immune therapy. Similar to observations seen in previous runs, the insufficient PD-L1 IHC results were most frequently characterized by a reduced proportion of PD-L1 positive cells compared to the level expected and defined by the NordiQC reference standard methods. This resulted in a too low TPS/CPS changing PD-L1 status in one or more of the carcinomas included. The companion diagnostic PD-L1 IHC assays, 22C3 GE006, Dako/Agilent and SP263 741-4905, Ventana/Roche performed in concordance to the product guidelines, were most successful providing a high proportion of sufficient and optimal results and superior to LD assays.
PD-L1 IC (TECENTRIQ®): 125 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 69% (52% optimal), being improved compared to the results in the two recent runs C7 and C8. The assessment for PD-L1 IC (TECENTRIQ®) focused on the evaluation of the analytical accuracy of the PD-L1 IHC assays to identify patients with urothelial carcinomas or triple negative breast carcinomas (TNBC) to be treated with TECENTRIQ® as immune therapy. In concordance with previous runs, the Ventana/Roche PD-L1 SP142 IHC assays 741-4860 and 790-4860 were most successful providing a pass rate of 91% and 93%, respectively. Other companion diagnostic and LD assays provided significantly lower pass rates - grouped together 6%. Insufficient results were most frequently characterized by a reduced proportion, too weak or false negative staining reaction of immune cells and/or combined with an excessive staining reaction of tumour cells compromising the scoring and evaluation of PD-L1 status in the immune cells.
Please note, that due to mis-alignment of two cores in the TMA and associated scoring sheet, data on scoring consensus will not be available in this run for PD-L1 IC.
July 9th 2021
Søren Nielsen
Scheme director

Run 61 (General module), B31 (Breast module) and H19 (HER2 ISH) were accomplished from January to April 2021. At present >550 participants from more than 60 different countries are registered in one or more of the modules offered.
The number of laboratories returning slides in due time for the assessment sessions decreased in this run 61 compared to previous assessments, and mainly caused to the COVID-19 pandemic and associated postal delays. All slides returned after the assessment were assessed and received advice if the result being insufficient but were not be included in the individual reports.
A short summary of the results is given below. Click on the epitope name to see the complete and detailed assessment report for the individual markers evaluated. In each assessment report, NordiQC intended to identify best practice methods and reliable and recommendable immunohistochemical critical assay performance controls (iCAPCs) to both guide the IHC protocol set-up and to monitor the IHC performance within the laboratories.
General module - run 61
CD15: 305 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 86% (53% optimal) being the highest level in all six assessments performed in NordiQC. 100% of insufficient results were characterized by generally too weak or false negative results for CD15.
CD56: 324 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 62% (36% optimal). The pass rate was significantly reduced compared to the latest assessment, run 37 2013. In this assessment, the rmAb clone MRQ-42 provided superior performance with a total pass rate of 99% (136/137) for both concentrated and RTU formats. This clone was very robust and provided a high proportion of optimal results on all main IHC platforms and by several different protocol settings. Due to the low pass rate, CD56 will be repeated in 2022, run 64 and thus no reassessment will be offered.
CDX2: 325 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 91% (79% optimal) being the highest level in all six assessments performed in NordiQC. The extended use of robust and successful Abs as rmAb clone EPR2765Y, access to optimally performing RTU systems from the main IHC system vendors and identification of pancreas as iCAPC seem to contribute to the improvement.
MSH6: 278 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 91% (79% optimal) and a significant improvement from run 52, 2018 with a pass rate of 52%. The access to several high quality RTU systems for MSH6 was instrumental for the improved pass rate. Especially the recently introduced RTU system of rmAb clone SP93 (Ventana/Roche) showed a significantly superior performance compared to the terminated system based on clone 44, being widely used in run 52.
p63: 324 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 79% (37% optimal). 97% of insufficient results were characterized by generally too weak or false negative results for p63. Efficient HIER preferable in combination with use of 3-step detection systems were main prerequisites for optimal p63 results. The widely use mAb clones DAK-p63 and 4A4 were significantly more successful compared to clone 7JUL.
Breast module - run B31
Estrogen receptor (ER): 378 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 85% (48% optimal). rmAb clones SP1 and EP1 and mAb clone 6F11 could all be used to provide an optimal result. 86% of the participants used RTU systems for the demonstration of ER. The RTU systems from Ventana/Roche and Dako/Agilent for BenchMark and Omnis respectively, were most successful with pass rates of 93 and 96%. Too weak or false negative staining reactions were the predominant features of insufficient results. Tonsil was found to be recommendable as positive and negative tissue control.
Progesterone receptor (PR): 377 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 92% (68% optimal). mAb clones 16, PgR 636, PgR 1294 and rmAb clone 1E2 could all be used to provide an optimal result. 77% of the participants used RTU systems for the demonstration of PR. The RTU systems from Ventana/Roche, Dako/Agilent and Leica Biosystems used as “plug-and-play” assays provided an overall pass rate of 99%. In this assessment, the insufficient results were mainly characterized by false negative results. Tonsil and uterine cervix in combination were found to be recommendable negative and positive tissue controls.
HER2 IHC: 362 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 92% (75% optimal). In this assessment, the CE-IVD approved HER2 IHC assays PATHWAY®, 4B5 (Ventana/Roche) and the recently launched HercepTest™ Dako/Agilent for Omnis were most successful providing a pass rate of 100%. LDTs based on a concentrate or RTU with no predictive claim were used by 24% giving a pass rate of 81% (39% optimal). The insufficient results were primarily characterized by false negative results or a poor signal-to-noise ratio compromising the interpretation.
HER2 ISH module - run H19
HER2 ISH: 143 laboratories participated in the technical assessment of HER2 ISH (BRISH) and obtained a pass rate of 70% (41% optimal) similar to the level obtained in most recent assessments. The VENTANA HER2 Dual ISH DNA Probe Cocktail, 800-6043 and INFORM™ HER2 Dual ISH assay, 800-4422/780-4422 were most widely used with pass rates of 75% and 64%, respectively. Insufficient results were mainly caused by large negative areas and missing signals.
Laboratories performing FISH (n=65) achieved a slightly higher consensus rate for the interpretation of HER2 amplification status compared to laboratories performing BRISH.
April 20th 2021,
Søren Nielsen
Scheme director
Run 60 (General module), B30 (Breast module), C8 (Companion modules) and H18 (HER2 ISH) module were completed from October to December 2020. In total, 485 laboratories participated in one or more of the modules offered.
Similar to the spring assessment, shipping of slides to and from the participants was challenged by the Covid-19 pandemic causing delays. Consequently, the overall participation rates were slightly reduced compared to normal levels. All slides returned after the specified assessment dates were assessed but not included in the general reports. The composition of assessor teams was also affected by travel restrictions limiting the possibility to include international assessors. Despite the challenge, all assessor teams were anchored on representation of both IHC expert pathologists and biomedical scientists primarily from Denmark. NordiQC is proud and grateful for the extensive support from our assessors and willingness to secure our core functions in such critical situations.
As described previously in news on 7th October, we were notified by some participants observing aberrant IHC results on slides circulated for especially p40 and PAX8. Completely false negative or uneven staining reactions were reported. This was most likely caused by quality issues on some of the SuperFrost Plus slides preventing reagents to spread. The issue was not seen by the internal validation process by NordiQC for any of the markers offered and in total during the assessments about 70 slides out of more than 2.600 slides assessed potentially were affected by technical quality of the slides circulated. For each assessment, slides characterized by uneven staining or a completely false negative result that might be related to the quality of the slide and not the protocol submitted, was given a comment in the individual assessment feed-back. We are in the process of evaluating if other glass types are superior to SuperFrost Plus slides for our EQA program with particular focus on the most common IHC platforms used by our participants, and we will circulate slides based on these findings in 2021.
As usual, a short summary of the results is given below. Click on the epitope name to see the complete and detailed assessment report for the markers evaluated. In each assessment report, NordiQC intended to identify best practice methods and reliable and recommendable immunohistochemical critical assay performance controls (iCAPCs) to both guide the IHC protocol set-up and to monitor the IHC performance within the laboratories.
General module - run 60
CD68: 329 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 83% (32 % optimal). The mAb clones PG-M1, KP1, 514H12 and rmAb clone GR021 could all be used to provide an optimal result for CD68. PG-M1 was most widely used and gave the highest proportion of optimal results both as concentrate within a laboratory developed (LD) assay and as Ready-To-Use (RTU) system. The Intended purpose of the assessment focused on general pathology to identify macrophages and lung pathology to differentiate macrophages from epithelial tumour cells as support for accurate read-out of PD-L1 TPS.
MLA: 312 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 88% (26% optimal) being the highest level seen in the NordiQC runs performed. The assessment focused on the use of MLA in the diagnosis of melanoma. The mAb clone A103 was the most widely used antibody for demonstration of MLA and applied by 88% of the laboratories. The pass rate was high both as concentrated format and as RTU system, but the level of optimal results was low at 18%. The relatively recently launched rmAb clone EP43, was most successful with a pass rate of 100%, 97% optimal.
p40: 262 laboratories participated. This was the third assessment of p40 in NordiQC and a pass rate of 86% was obtained, which is a significant increase compared to the result obtained in the previous runs. The increased pass rate may be explained by an extended use of the highly sensitive and robust mAb clone BC28 both as concentrate and as RTU format. Additionally, the proportion of laboratories using less successful polyclonal antibodies has been reduced from 41% in run 44 to 7% in this run. The identification of tonsil and placenta as reliable iCAPCS has facilitated the process to calibrate and monitor the performance of IHC assays for p40.
PAX8: 271 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 39% (11% optimal). The pass rate has thus in two successive runs been at a very low level. The low pass rate was especially related to extended use of the less successful mAb clone MRQ-50 providing a poor performance on the Ventana BenchMark and Dako Omnis platforms and in addition cross-reaction with PAX5 in B-cells. In contrast, the rmAbs clones EP298 and SP348 gave encouraging results and a high proportion of sufficient results on the main fully automated platforms and no cross-reaction with e.g. PAX5 was observed. Due to the low pass rate in the two runs, PAX8 will be repeated in run 62, 2021 and consequently no re-assessment offered for run 60.
SOX10: 250 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 92% (67% optimal) being the highest level seen in the four NordiQC runs performed. The assessment focused on the use of SOX10 identifying malignant melanomas and triple negative breast carcinoma in the characterization of tumours of unknown origin. The Ventana RTU system based on the rmAb clone SP267 for BenchMark was most successful providing a pass rate of 98%, 95% optimal when applied by recommended protocol settings.
Breast module - run B30
ER: 363 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 94% (58% optimal). rmAb clones SP1 and EP1 and mAb clone 6F11 could all be used to provide an optimal result. 86% of the participants used RTU systems for the demonstration of ER. In this assessment, low analytical sensitivity giving a too weak or false negative staining reaction was the predominant feature of insufficient results. Tonsil was found to be recommendable as positive and negative tissue control with particular possibility to ensure an appropriate low limit of demonstration of ER – concordant to the ASCO/CAP 2020 recommendations on ER IHC testing.
HER2 IHC: 343 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 92% (63% optimal). In this assessment, the FDA-/CE-IVD approved HER2 IHC assay PATHWAY® /4B5 Ventana/Roche was the most accurate and successful assays providing a pass rate of 99% and 97%, respectively. LD assays based on concentrated Abs or generic RTU Abs without predictive claim were used by 25% and for this group a pass rate of 80% was obtained. The insufficient results primarily characterized by false negative results or a poor signal-to-noise ratio compromising the interpretation.
HER2 ISH module - run H18
HER2 ISH: 141 laboratories participated in the technical assessment of HER2 ISH and obtained a pass rate of 69% (40% optimal). In this assessment an increased number of participants used the VENTANA HER2 Dual ISH DNA Probe Cocktail, 800-6043 providing a pass rate of 80% on the expense of the less successful INFORM™ HER2 Dual ISH assay, 800-4422/780-4422 with a pass rate of only 38%. In total 94% of the participants used one of these two, Ventana ISH systems. The insufficient results were mainly characterized by large negative areas and missing signals. 61 laboratories submitted a FISH result and participated in the interpretation segment. Laboratories performing FISH achieved a slightly higher consensus rate for the interpretation of HER2 amplification status compared to laboratories performing BRISH.
Companion module - run C8
PD-L1 KEYTRUDA: 200 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 86% (49% optimal). This assessment for PD-L1 KEYTRUDA® primarily focused on the evaluation of the analytical accuracy of the IHC assays to identify patients with NSCLCs and urothelial carcinomas to be treated with KEYTRUDA® as immune therapy. Similar to observations seen in previous runs, the insufficient PD-L1 IHC results were most frequently characterized by a reduced proportion of PD-L1 positive cells compared to the level expected and defined by the NordiQC reference standard methods. This resulted in a too low TPS/CPS changing PD-L1 status in one or more of the carcinomas included. The companion diagnostic PD-L1 IHC assays, 22C3 GE006, Dako/Agilent and SP263 741-4905, Ventana/Roche performed in concordance to the product guidelines, were most successful providing a high proportion of sufficient and optimal results and superior to LD assays.
PD-L1 TECENTRIQ: 123 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 63% (33% optimal), being slightly improved compared to run C7 with a pass rate of 55%. The assessment for PD-L1 TECENTRIQ® primarily focused on evaluation of the analytical accuracy of the PD-L1 IHC assays to identify patients with urothelial carcinomas or triple negative breast carcinomas (TNBC) to be treated with TECENTRIQ® as immune therapy. The PD-L1 SP142 CDx IHC assay product no. 741-4860 and the IHC assay 790-4860 from Ventana/Roche were the most successful assays. Other PD-L1 CDx assays as SP263 (741-4905, Ventana) and 22C3 (SK006/GE006, DakoAgilent) being very successful in the NordiQC PD-L1 KEYTRUDA® assessments provided no sufficient staining results. The insufficient results were typically characterized by a too strong staining reaction in tumour cells in one or more of the carcinomas compromising the interpretation of PD-L1 reaction in immune cells.
December 14th, 2020
Søren Nielsen,
Scheme director

Run 60 (General module), B30 (Breast module), C8 (Companion module) and H17 (HER2 ISH) is now being executed.
Due to the Covid-19 pandemic and transportation challenges for postal services, we anticipate delays for slides to be returned to NordiQC for the official assessment dates. We will do our very best to assess all slides returned, but due to the extensive data analysis, only slides received and available for the assessment of the individual modules will be integrated in the assessment reports.
We have been informed by some laboratories, that slides for p40 and PAX8 have revealed aberrant properties producing uneven staining and/or completely negative results. During the internal NordiQC validation of the circulated material, we did not observe any issues and subsequent retests have not provided any transparency of the problem. However, the problems are most likely related to change in the hydrophilic character of the SuperFrost Plus slides to be more hydrophobic and hereby preventing reagents to spread. We are now in the process to validate new slides for our EQA program and hopefully will identify slides with improved consistency.
In this assessment, slides returned to NordiQC with clear indication of aberrant results caused by the slide properties will be marked as “technically insufficient” and not assessed. We will shortly after the assessment explore the option to resend new slides to the laboratories being affected by this issue. We apologize for any inconvenience.
Søren Nielsen Scheme director

NordiQC is now present on LinkedIn and the portal will be used to share news and activities related to our organization. Follow us here:
https://www.linkedin.com/company/nordiqc
Run 59 (General module) and C7 (Companion modules) were accomplished from April to July 2020. In total, 366 laboratories participated in one or more of the modules offered.
The assessments were affected by the Covid-19 pandemic and especially the shipping of slides to and from the participants was challenged. The overall participation rates were reduced to 80-90% compared to 95-98%, normally seen. However, for all markers adequate number of laboratories and data points were accomplished to generate assessment reports and conclusions. All slides returned will be assessed but not be included in the online available reports.
As usual, a short summary of the results is given below. Click on the epitope name to see the complete and detailed assessment report for the individual markers evaluated. In each assessment report, NordiQC intended to identify best practice methods and reliable and recommendable immunohistochemical critical assay performance controls (iCAPCs) to both guide the IHC protocol set-up and to monitor the IHC performance within the laboratories.
General module - run 59
ASMA: 260 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 69% (28 % optimal) being the highest level in all six NordiQC assessment runs for ASMA. The Ready-To-Use (RTU) systems from Dako and Leica based on the mAb clones 1A4 and asm-1, respectively were most successful. The mAb clone 1A4 provided an inferior performance on the Ventana BenchMark platforms both as concentrate within a laboratory developed (LD) assay and as Ready-To-Use (RTU) system. The recently launched mAb clone BS66 showing promising performance in previous assessments and used within the NordiQC reference standard methods for ASMA, was less successful giving unreproducible and unspecific results. The product was during the assessment terminated by the vendor due to lot-to-lot inconsistency.
CD10: 295 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 79% (57% optimal). The assessment focused on CD10 as part on an IHC panel discriminating Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL) of Germinal centre B-cell like (GCB) from non-GCB subtype. The well-established and widely used mAb clone 56C6 was most successful both within a LD assay and especially as RTU system from Dako and Leica. HIER in alkaline buffer, precise calibration of the primary Ab and use of a 3-step polymer or multimer based detection system were the main prerequisites for an optimal result.
CD45: 296 laboratories participated. This was the third assessment of CD45 in NordiQC and a pass rate of 94% was obtained, which is a significant increase compared to the result obtained in the previous runs. The use of robust primary Abs (e.g. mAb clones 2B11+PD7/26) but also well calibrated RTU systems accounted for the superior performance obtained in this assessment. The identification of tonsil and liver as reliable iCAPCS has facilitated the process to calibrate and monitor the performance of IHC assays for CD45.
p16: 291 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 83% (50% optimal). This was the second assessment of p16 in NordiQC and the pass rate increased from 70% seen in run 26, 2009. The assessment focused on p16 identifying HPV associated cervical lesions in histological uterine cervical samples. 78% of the participants used the established Ventana CINtec® RTU products based on mAb clone E6H4 giving a pass rate of 100% when applied as “Plug-and-Play” system. In 2019 and 2020 many new Abs have been launched and especially the mAb clone MX007 was found successful. The mAb clone G175-405 showed an inferior and unsatisfactory performance.
S100: 299 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 82% (48% optimal) and identical to the pass rate in the recent run 50, 2017. The assessment focused on S100 used to identify the origin of melanomas of cancer of unknown primary (CUP) and differentiate schwannoma from other spindle cell lesions as leiomyoma. In general, pAbs were more successful than mAbs both within LD assays based on concentrated formats or as RTU systems. Especially the Dako RTU systems provided a high pass rate and proportion of optimal results. An increased number of participants use RTU systems, 58% in this run compared to 46% in run 50, most likely caused by the “gold-standard” S100 pAb Z0311, Dako not being commercially available anymore.
URO II/III: 66 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 45% (21% optimal). This was the first assessment of URO II/III in NordiQC and focused on identification of urothelial origin of cancer of unknown primary (CUP). The relatively low pass rate was especially related to extended use of less successful Abs and in particular related to Abs against URO III. In contrast the mAb clone BC21 was very successful and in total used by 47% of the participants either as concentrated format or as RTU giving an overall pass rate of 87% (45% optimal). Urethra and tonsil in combination seem appropriate as central positive and negative tissue controls to calibrate and monitor the performance of IHC assay for URO II/III.
Companion module - run C7
PD-L1 KEYTRUDA®: 191 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 83% (55% optimal). This assessment for PD-L1 KEYTRUDA® primarily focused on the evaluation of the analytical accuracy of the IHC assays to identify patients with NSCLCs and urothelial carcinomas to be treated with KEYTRUDA® as immune therapy. Similar to the observations seen in previous runs, the insufficient PD-L1 IHC staining results were most frequently characterized by a reduced proportion of PD-L1 positive cells compared to the level expected and defined by the PD-L1 IHC pharmDx assay, SK006 (Dako/Agilent). This resulted in a too low TPS/CPS changing the PD-L1 status in one or more of the carcinomas included in the assessment material. The companion diagnostic PD-L1 IHC assays, 22C3 GE006, Dako and SP263 741-4905, Ventana performed in concordance to the product guidelines, were most successful providing a high proportion of sufficient and optimal results and superior to LD assays.
PD-L1 TECENTRIQ®: 102 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 55% (30% optimal), being significantly reduced from the results in the first run C7 with a pass rate of 76%. The assessment for PD-L1 TECENTRIQ® primarily focused on evaluation of the analytical accuracy of the PD-L1 IHC assays to identify patients with urothelial carcinomas or triple negative breast carcinomas (TNBC) to be treated with TECENTRIQ® as immune therapy. In concordance to run C6, the PD-L1 SP142 companion diagnostic IHC assay 741-4860 from Ventana was most successful providing a pass rate of 93%. Other companion diagnostic and LD assays provided significantly lower pass rates - grouped together 18%. insufficient results were most frequently characterized by a reduced proportion or too weak specific staining reaction of immune cells combined with an excessive staining reaction of tumour cells compromising the scoring and PD-L1 status in the immune cells.
July 10th 2020
Søren Nielsen, Scheme director

Run 58 (General module), B29 (Breast module) and H17 (HER2 ISH) were accomplished from January to April 2020. In total 448 laboratories participated in one or more of the modules offered.
A short summary of the results is given below. Click on the epitope name to see the complete and detailed assessment report for the individual markers evaluated. In each assessment report, NordiQC intended to identify best practice methods and reliable and recommendable immunohistochemical critical assay performance controls (iCAPCs) to both guide the IHC protocol set-up and to monitor the IHC performance within the laboratories.
Please note, table 1 has been adjusted. The table now displays the percentage of sufficient and optimal results for a specific antibody (last two rows right). Due to the expanded use of antibodies for Ready-To-Use systems, table 1 now shows the performance of these systems when used by vendor recommended protocol settings (VRPS) or by laboratory modified protocol settings (LMPS).
General module - run 58
CK-PAN: 326 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 75% (52% optimal). The pass rate and performance was highly influenced by choice of the antibody (Ab), retrieval method and IHC platform used. The mAb clone cocktail AE1/AE3 provided a high pass rate and proportion of optimal results when used with HIER both as concentrate within a laboratory developed (LD) assay and as Ready-To-Use (RTU) system assay, whereas the clone cocktail AE1/AE3/PCK26 required a combined pre-treatment with HIER and gentle proteolysis for optimal performance. The clones MNF116 and Oscar showed an inferior performance and cannot be recommended as CK-PAN primary Ab.
TTF1: 322 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 80% (56% optimal) being the highest level in all seven NordiQC assessment runs for TTF1. In concordance with previous NordiQC assessments for TTF1, the mAb clone SPT24 and the rmAb clone SP141 were most successful providing an overall pass rate of 87% and 99%, respectively (all protocol settings). In contrast, mAb clone 8G7G3/1 was less successful with a significantly lower pass rate of 20%. In particular, the increased use of the successful clones at the expense of 8G7G3/1 seemed to have a positive impact on the pass rate in this assessment. The RTU systems from Ventana (rmAb SP141) and Leica (mAb SPT24) was most successful, both providing a pass rate of 100% when used in compliance with vendor recommended protocol settings.
MUM1: 259 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 73% (46% optimal). The pass rate was highly influenced by the choice of the antibody (Ab). The well established clone MUMp1 was most successful both within a LD assay and as RTU system from Dako/Agilent. The Dako/Agilent RTU system provided an overall pass rate of 98% when used as “plug-and-play”. In contrast, a pass rate of 1% was observed for the mAb clone MRQ-43 being used by 13% of the participants.
NKX3.1: 107 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 82% (55% optimal). This was the second assessment of NKX3.1 in NordiQC and the pass rate increased from 65% seen in run 49, 2017. The rmAb clone EP356 was used by 66% of all participants and an optimal result could be obtained both within a LD assay and as a RTU system. Efficient HIER in an alkaline buffer and use of a sensitive and specific 3-step polymer / multimer based detection system gave the highest proportion of optimal results. The identification and use of testis as iCAPC for NKX3.1 seem to be supportive to monitor the level of analytical sensitivity as Sertoli cells express low-levels NKX3.1.
SATB2: 105 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 58% (33% optimal). This was the first assessment of SATB2 in NordiQC and focused on identification and characterization of colorectal carcinomas and neuroendocrine tumours. The relatively low pass rate was related to extended use of less successful Abs and not adequately calibrated IHC protocols. The rmAb clones EP281 and SP281 were most successful providing an optimal performance by the use of efficient HIER in an alkaline buffer and a 3-step detection system. Appendix, tonsil and testis were observed to be recommendable positive and negative tissue controls to monitor the level of analytical sensitivity and specificity.
Breast module - run B29
Estrogen receptor (ER): 367 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 94% (66% optimal). rmAb clones SP1 and EP1 and mAb clone 6F11 could all be used to provide an optimal result. 83% of the participants used RTU systems for the demonstration of ER. The RTU systems from Ventana, Dako and Leica used as “plug-and-play” assays provided an overall pass rate of 96%. In this assessment, a too weak or false negative staining reaction was the predominant feature of insufficient results. Tonsil was found to be recommendable as positive and negative tissue control.
Progesterone receptor (PR): 365 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 90% (53% optimal). mAb clones 16, PgR 636, PgR 1294 and rmAb clone 1E2 could all be used to provide an optimal result. 79% of the participants used RTU systems for the demonstration of PR. The RTU systems from Ventana, Dako and Leica used as “plug-and-play” assays provided an overall pass rate of 98%. In this assessment, the insufficient results were mainly characterized by false positive results. This in particular being observed for off-label use of the Ventana RTU system based on rmAb 1E2. Tonsil and uterine cervix in combination were found to be recommendable negative and positive tissue controls.
HER2 IHC: 344 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 93% (78% optimal). In this assessment, the FDA-/CE-IVD approved HER2 IHC assays HercepTest™ and PATHWAY® /4B5 were most the most accurate and successful assays providing a pass rate of 100% and 97%, respectively. LD assays were used by 25% and for this group a pass rate of 79% was obtained. The insufficient results primarily characterized by false negative results or a poor signal-to-noise ratio compromising the interpretation.
HER2 ISH module - run H17
HER2 ISH: 133 laboratories participated in the technical assessment of HER2 (BR)ISH and obtained a pass rate of 75% (43% optimal). In this assessment, an increased pass rate especially compared to the latest run H16, but also to the recent runs, was seen. One of the contributing factors seems to be related to the expanded use of the VENTANA HER2 Dual ISH DNA Probe Cocktail, 800-6043 providing a pass rate of 80% on the expense of the less successful INFORM™ HER2 Dual ISH assay, 800-4422/780-4422 with a pass rate of 66%. In total 92% of the participants used one of these two, Ventana ISH systems. The insufficient results were mainly characterized by large negative areas and missing signals.
April 20th 2020
Søren Nielsen
Scheme director

It is with severe despondency and disappointment we hereby inform that we have decided to cancel the 4th NordiQC International conference planned 2-5th of June 2020. The global uncertainty and extensive travel restrictions related to covid-19 have had a tremendous impact on registrations for the conference, which has been status quo for more than 3 weeks now. The uncertainty has unfortunately and of central decisive importance for the cancellation also affected many of our speakers not being able to provide a definite confirmation of their presence. At present the incidence rate increases dramatically in Denmark and Europe and expected to continue with more restrictions to come concerning travel and meetings. We hereby have been put in a very risky situation to either postpone the cancellation of the conference to last minute due to no improvements for the covid-19 epidemic or to have a conference with a very reduced number of participants/speakers and hereby an abridged scientific meeting compared to the level expected from all stakeholders of our conference.
We hope that the conclusion to cancel the conference at this point is considered as due diligence, as we want to reduce the uncertainty and negative impacts related to the decision.
NordiQC reimburses all registration fees and sponsorship payments. If payment has been performed by bank account transfer, please send bank account data to us with registration number, IBAN and SWIFT codes.
Please receive our deepest apologies for all inconveniences.
Søren Nielsen
NordiQC director
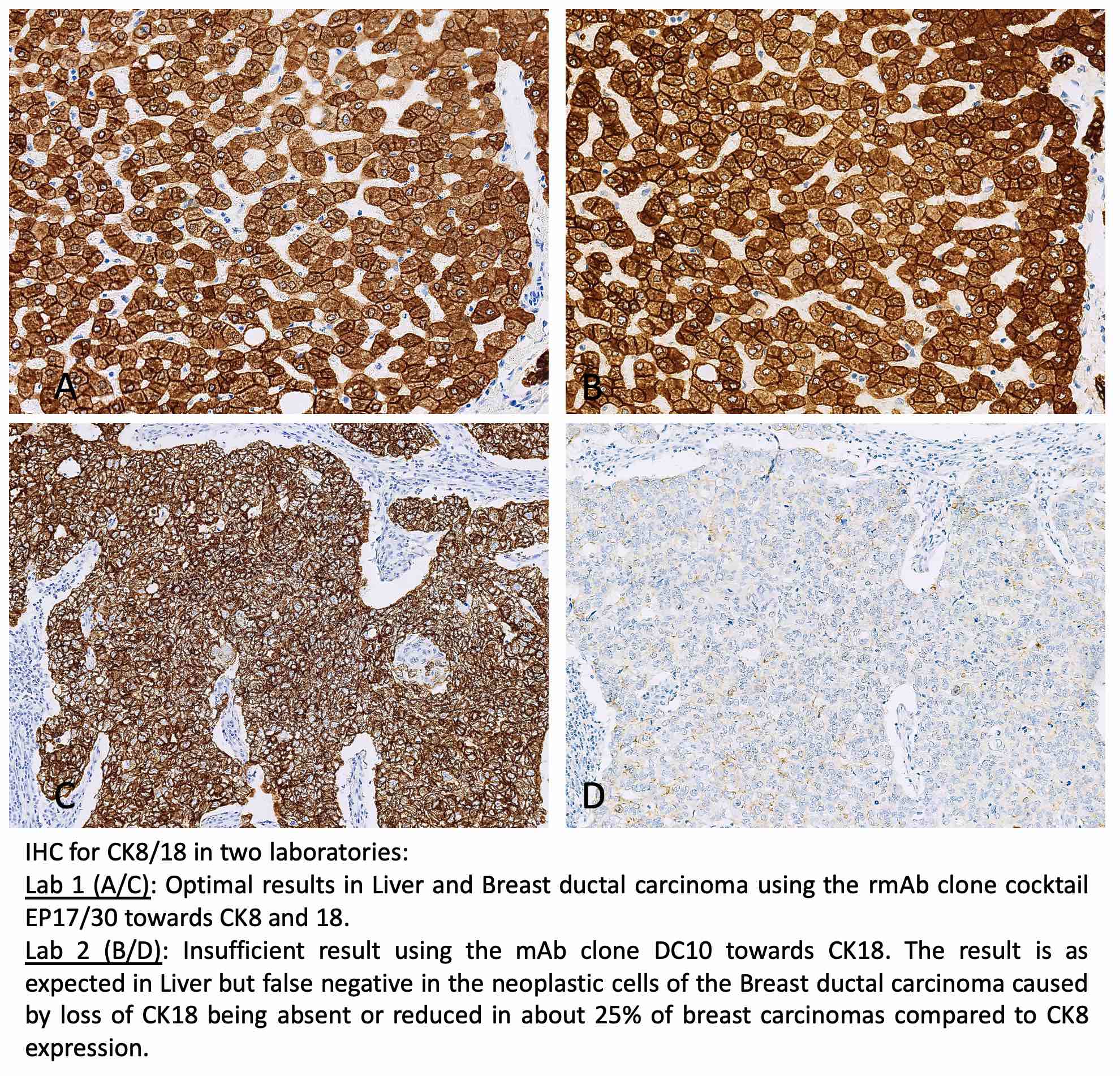
Run 57, B28, H16 and C6 were accomplished from August to December 2019. In total, 450 laboratories participated in one or more of the modules offered. For the first time PD-L1 IHC assessment was segmented in PD-L1 KEYTRUDA® and PD-L1 TECENTRIQ® to align IHC test to treatment choice, cancer indications and scoring algorithms.
A short summary of the results is given below. Click on the epitope name to see the complete and detailed assessment report for the individual markers evaluated. In each assessment report, NordiQC intended to identify best practice methods and reliable and recommendable immunohistochemical critical assay performance controls (iCAPCs) to both guide the IHC protocol set-up and to monitor the IHC performance.
General module - run 57
ALK (lung): In total, 201 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 84% (59% optimal). The mAb clone OTI1A4 and the rmAb clone D5F3 could both be used to provide an optimal staining result. To low concentration of the primary Ab and use of detection systems with low sensitivity were the main causes of insufficient staining reactions. The mAb clone ALK1, although useful when detecting translocations in lymphomas, cannot be used when detecting translocations in lung adenocarcinomas (and Merkel cell carcinomas) since it provides too low analytical sensitivity.
Bcl-2: In total, 319 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 89% (64% optimal). Overall a very high pass rate and proportion of optimal results were observed. The well established clones as 124 and BCL2/100/D5 were most successful especially when applied within Ready-To-Use (RTU) systems e.g. from Dako/Agilent and Leica providing a pass rate of 100%. The rmAb clones E17 and EP36 unexpectedly showed an inferior performance and gave a negative reaction in one of the follicular lymphomas with t(14;18)(q32;q21) translocation.
Cytokeratin 8/18: In total, 238 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 66% (41% optimal). The pass rate was highly influenced by the choice of the antibody (Ab). The clone cocktails against CK8/18 B22.1/B23.1 and EP17/30 and clone EP17 against CK8 were most successful both used within a laboratory developed (LD) assay or as RTU system. Abs towards CK18 showed an inferior performance in the included breast carcinoma due to partial loss of CK18 emphasizing the benefit to use Abs towards both CK8 and 18 for the identification of adenocarcinoma origin in tumour classification.
MSH2: 258 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 81% (53% optimal). The RTU systems for MSH2 from the two main vendors, Dako and Ventana both provided higher pass rates compared to LD assays. For optimal performance using these two RTU systems, protocols based on the vendor recommended settings were more successful compared to laboratory modified settings. This was seen e.g.for the Dako RTU system IR085 based on mAb clone FE11 with intended use for Autostainer Link 48. Using the RTU system according to the vendor recommended protocol, a pass rate of 100% was seen (86% optimal). If the RTU format IR085 was used by modified protocol settings, the pass rate was 87%, 56% optimal.
SMAD4: 52 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 42% (31% optimal). This was the first assessment of SMAD4 in NordiQC and focused on the use of IHC for identification of loss of SMAD4 expression caused by inactivation of the SMAD4 gene seen in e.g. pancreatic adenocarcinomas. The rmAb clone EP618Y was most successful and provided an optimal result on most IHC platforms, whereas the mAb clone B8 showed an inferior performance on the fully automated platforms from Dako (Omnis) and Ventana (BenchMark). Efficient HIER in an alkaline buffer and use of 3-step detection systems were main prerequisites for optimal demonstration of SMAD4.
Breast module - run B28
Estrogen receptor (ER): 367 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 93% (51% optimal). rmAb clones SP1 and EP1 and mAb clone 6F11 could all be used to provide an optimal result. The RTU systems from Ventana, Dako and Leica used as “plug-and-play” assays provided an impressive pass rate of 99%. In this assessment, a too weak or false negative staining reaction was the predominant feature of insufficient results, but also false positive results were observed.
HER2 IHC: 346 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 86% (72% optimal). In this assessment, the FDA-/CE-IVD approved HER2 IHC assays HercepTest™ and PATHWAY® /4B5 were most successful and especially when used in concordance with the recommended protocol settings providing an overall pass rate of 90%. LD assays were used by 25% and for this group a pass rate of 65% was obtained. The insufficient results were characterized by both false negative and false positive results.
HER2 ISH module - run H16
HER2 ISH: 137 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 54% (39% optimal). Despite optimal protocol settings, a high proportion of technical insufficient results were seen, indicating that technical issues are influencing the quality and reproducibility of the BRISH assays. The most commonly used HER2 BRISH assay, INFORM™ HER2 Dual ISH 800-4422 / 780-4422 (Ventana/Roche), only provided a pass rate of 54% despite using appropriate, well-characterized protocol settings. The newly launched HER2 BRISH assay INFORM™ HER2 Dual ISH 800-6043 (Ventana/Roche) was more successful giving a pass rate of 84% when used by optimal protocol settings.
Companion module – C6
PD-L1 KEYTRUDA®: 182 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 75% (46% optimal). This assessment for PD-L1 KEYTRUDA® primarily focused on the evaluation of the analytical accuracy of the IHC assays performed by the NordiQC participants to identify patients with NSCLCs and urothelial carcinomas to be treated with KEYTRUDA® as immune therapy. The CE IVD approved companion diagnostic assays as 22C3 SK006/GE006 Dako, 28-8 SK005 Dako and SP263 Ventana provided an overall pass rate of 89%, when used accordingly to package inserts. LD assays were widely applied by 60% of the participants. The overall pass rate for LD assays was 66%. The prevalent feature of insufficient results was characterized by false negative staining results changing the expected TPS or CPS status.
PD-L1 TECENTRIQ®: 84 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 76% (40% optimal). This assessment for PD-L1 TECENTRIQ® primarily focused on evaluation of the analytical accuracy of the PD-L1 IHC assays performed by the participating laboratories to identify patients with urothelial carcinomas or triple negative breast carcinomas (TNBC) to be treated with TECENTRIQ® as immune therapy. The PD-L1 SP142 companion diagnostic IHC assays from Ventana were most successful assays providing a pass rate of 94%. Other companion diagnostic assays and LD tests provided significantly lower pass rates of 67% and 65%, respectively. Insufficient results were typically characterized by a too strong staining reaction in tumour cells compromising the interpretation of immune cells.
ASMA
NordiQC has performed a revised assessment of ASMA run 55, 2019. In the original assessment, we observed a very low pass rate of only 17% and significantly inferior to the expected and obtained in previous runs. The assessment criteria were primarily focusing on the level of technical sensitivity and to a less extent on the diagnostic utility of IHC for ASMA. In the assessment a sufficient result required a positive staining in the GIST specimen and a negative staining reaction in this tumour thus lead to in an insufficient mark despite an otherwise optimal result obtained in all other tissues including the NordiQC recommended positive and negative tissue controls.
The revised assessment of ASMA addressed both the technical level of sensitivity and primary diagnostic purpose of IHC for ASMA e.g. demonstration of ASMA in leiomyogene neoplasias. The pass rate in the revised assessment for ASMA was 58% and comparable to previous assessments for ASMA. However, only 9% were optimal and this still indicates an improved performance for ASMA should be required.
The revised requirements and criteria for optimal performance were as applied in the original assessment but accepting a negative staining reaction of the GIST tumour as sufficient (good) provided that the IHC assays performed as expected (good or optimal) in all other tissue cores.
Due to the low pass rate in run 55, many laboratories have asked for re-assessment of their IHC protocol in case of an insufficient result. These laboratories will receive a revised assessment mark for both the original submitted slide in run 55 and for the slide for re-assessment.
Do not hesitate to contact NordiQC in need for clarifying questions.
At this point we also want to inform that we will repeat assessment for ASMA in run 59, 2020.
December 13th 2019
Søren Nielsen
Scheme director

Run 56 (General module) and C5 (Companion module for PD-L1 NSCLC and Urothelial carcinoma) were accomplished from April to July 2019. In total 356 laboratories participated in one or both of the modules offered. For the first time, PD-L1 IHC testing also focused on Urothelial carcinoma in addition to NSCLC.
A short summary of the results is given below. Click on the epitope name to see the complete and detailed assessment report for the individual markers evaluated. In each assessment report, NordiQC intended to identify best practice methods and reliable and recommendable immunohistochemical critical assay performance controls (iCAPCs) to both guide the IHC protocol set-up and to monitor the IHC performance.
General module - run 56
C-MYC: 173 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 57% (24% optimal). This was the first assessment of C-MYC in NordiQC and focused on the use of IHC for C-MYC in lymphoma classification. The rmAb clones EP121 and Y69 could both be used to provide optimal results. Efficient HIER in an alkaline buffer and use of 3-step detection systems were main prerequisites for optimal demonstration of C-MYC. Laboratory developed (LD) assays based on one of these two Abs were more successful than corresponding Ready-To-Use (RTU) systems.
CD117: 312 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 87% (48% optimal). As seen in the previous assessments, the recently launched rmAbs EP10 and YR145 were most successful providing an overall pass rate of 97%, 78% optimal. The extended use of these Abs and implementation of best practice protocols for well established Abs such as the pAb 4502 have contributed to an increased pass rate compared to previous assessments.
EpCAM: 256 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 57% (34% optimal). Despite an increased pass rate compared to previous runs, the level was still low. For optimal performance, the selection of Ab must be made with focus on the IHC platform and reagents available in the laboratory. The most commonly used mAb clone Ber-EP4 require HIER in a special formulated buffer available for Dako IHC platforms and here provides high pass rates both within LD assays or as RTU system. On e.g. the Ventana BenchMark IHC platforms, mAb clones BS14 and VU-1D9 had significantly higher pass rates compared to mAb clone Ber-EP4.
Melan A (MLA): 286 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 65% (24% optimal). This assessment primarily addressed the performance in melanocytic lesions and not steroid hormone related lesions, only being relevant for mAb clone A103. mAb clone A103 was the most widely used Ab both within LD assays or RTU systems. For optimal performance, efficient HIER in an alkaline buffer and use of a sensitive and specific 3-step detection system were found to be essential. The RTU system IR/IS633 Dako based on mAb clone A103 for Autostainer Link 48 was most successful providing a pass rate of 100%, 58% optimal when using recommended protocol settings. The newly launched rmAb clone EP43 gave a promising performance and optimal results on all main IHC platforms.
Mismatch repair protein 1 (MLH1): 259 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 90% (64% optimal). A significantly increased pass rate was seen in this run compared to run 49, 2017 (59%). The RTU systems for MLH1 from the three main vendors, Dako, Leica and Ventana all provided higher pass rates compared to LD assays. For optimal performance using RTU systems, protocols based on the vendor recommended settings were more successful compared to laboratory modified settings. This was seen e.g.for the Dako RTU system IR/IS079 based on mAb clone ES05 with intended use for Autostainer Link 48. Using the RTU system according to the vendor recommended protocol, a pass rate of 100% was seen (93% optimal). If the RTU format IR/IS079 was migrated to Dako Omnis using same protocol settings, the pass rate was 77%, 27% optimal.
Paired box gene-8 protein (PAX8): 264 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 37% (12% optimal.) A surprisingly low pass rate was observed. 98% of the insufficient results were characterized by a generally too weak or false negative staining reaction in cells expected to be demonstrated. The combination of using challenging tissues with critical clinically relevant PAX8 expression levels and an extended use of Abs (e.g. clone MRQ-50) being less successful on the Ventana BenchMark and Dako Omnis platforms (used by the majority of all participants) had a negative impact on the pass rates.
Companion module - run C5
PD-L1 (lung): 176 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 80% (51% optimal). The assessment primarily focused on the accuracy of the PD-L1 IHC assays for TPS status in NSCLCs to guide treatment with KEYTRUDA®. The CE IVD approved companion diagnostic assays as 22C3 SK006/GE006 Dako and SP263 Ventana provided a pass rate of 92% and 91%, respectively, when used accordingly to package inserts. LD assays were widely applied by 63% of the participants. The overall pass rate for LD assays was 74%. The prevalent feature of insufficient results was characterized by false negative staining results changing the TPS status from high to low or low to negative.
PD-L1 (uro): 93 laboratories participated and obtained a pass rate of 76% (50% optimal). The assessment focused on the accuracy of the PD-L1 IHC assays for CPS status in Urothelial carcinomas to guide treatment with KEYTRUDA®. Similar to PD-L1 IHC for NSCLC, companion diagnostic assays provided a superior pass rate compared to LD assays. LD assays was used by 66% of the participants and an overall pass rate of 70% was seen. This was in contrast to the Dako pharmDx 22C3 PD-L1 SK006 that provided a pass rate of 91%.
July 9th 2019
Søren Nielsen
Scheme director
PD-L1 IHC testing has a significant impact on patient eligibility for tailored specific immune oncology and require diagnostic accuracy. This also underlines the need of appropriate EQA methods to evaluate the performance of PD-L1 IHC testing among the participating laboratories.
At present, PD-L1 IHC testing is based on the alignment of treatment choice / cancer indication / IHC test method including scoring algorithms. This means that is mandatory to focus on the purpose of a PD-L1 test to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy and adequacy. Based on this NordiQC intends, from run C6 and onwards, to offer 2 segments in the companion module for PD-L1 IHC testing;
- One segment focusing on PD-L1 IHC in NSCLC and Urothelial carcinoma for treatment with KEYTRUDA®. Laboratories must score the stained slides using the associated TPS- and CPS scoring systems.
- One segment focusing on PD-L1 IHC in triple negative breast cancer and Urothelial carcinoma for treatment with TECENTRIQ®. Laboratories must score the stained slides using the associated IC-scoring system.
The diagnostic accuracy will be evaluated on the participants performance compared to “gold standard / reference standard” methods and results characterized by the respective associated and approved companion diagnostic PD-L1 IHC assays and relevant scoring methods / cut-offs. The participants can use both laboratory developed and companion diagnostic assays for PD-L1 but need to specify for which purpose. The modification and updated segmentation of PD-L1 IHC testing will enable NordiQC to give more valuable information to the participants on their diagnostic accuracy. There are many additional purposes including different treatment options for PD-L1. At this point NordiQC has decided to focus on the most widely tested areas in PD-L1 IHC testing but will update the segmentation accordingly to any changes being required.
Søren Nielsen
Scheme director

Run 55 (General module), B27 (Breast cancer IHC module), and H15 (HER2 ISH module) were accomplished December 2018 – April 2019. A very short summary of the results is given below. Click on the epitope name to see the complete general assessment results for each marker, including major causes of insufficient results, immunohistochemical critical assay performance controls (iCAPCs), and recommendable clones and protocols. Individual results are available after login on the homepage.
General module - run 55
Alpha-smooth mucle antigen (ASMA): 281 labs participated, 17% sufficient, 9% optimal based on a very challenging test material. mAb clone BS66 as concentrate gave optimal results in all of 7 cases. The most used mAb clone 1A4 could only give optimal results with the Dako Autostainer and Leica Bond platforms. rmAb clone EP188 could give optimal results on the Ventana platform with a combined proteolytic and heat induced pretreatment.
Bcl-6: 279 labs participated, 77% sufficient, 45% optimal. The mAb clones PG-B6p and LN22 provided the highest proportion of sufficient and optimal results applied as an RTU format (Dako and Leica, respectively). The RTU system based on the mAb clone GI191E/A8 (Ventana) provided a lower pass rate and was challenged by poor signal-to-noise ratio and false positive results.
Cytokeratin 5 (CK5): 263 labs participated, 44% sufficient, 25% optimal. Optimal staining results could be obtained with the mAb clone XM26, and the rmAbs clones BSR55, EP24and SP27used as concentrates. However, SP27 has in NordiQC studies (unpublished) shown positive reaction in lung adenocarcinomas being negative for other CK5 antibodies as well as p40. The significance of this is currently uncertain. The ascites produced mAb clone D5/16 B4 was less successful due to low analytical sensitivity in combination with the risk of false positive “Mouse Ascites Golgi” staining reaction.
SOX10: 204 labs participated, 89% sufficient, 68% optimal. The mAb clones BC34, BS7, ZM10, and the rmAb clones EP268 and SP267 could all be used to obtain optimal results for SOX10 with appropriate protocols. The RTU system 760-4968 (Ventana) based on the rmAb clone SP267, showed superior performance.
Wilms’ tumour-1 protein (WT1): 291 labs participated, 90% sufficient, 60% optimal. The mAb clones 6F-H2, WT49 and the rmAb clones EP122 and D8I7F are all recommendable antibodies with appropriate protocols. A combined HIER–protease retrieval protocol provided a significant improvement in the signal-to-noise ratio for the mAb clone 6F-H2 on the Ventana platform (both as concentrate and RTU system).
Breast cancer IHC module - run B27
Estrogen receptor (ER): 348 labs participated, 90% sufficient, 54% optimal. rmAb clones SP1 and EP1 and mAb clone 6F11 could all be used to provide an optimal result. The corresponding Ready-To-Use (RTU) system from Ventana/Roche (rmAb SP1) provided the highest proportion of sufficient and optimal results.
HER2 IHC: 324 labs participated, 86% sufficient, 83% optimal. The laboratory modified protocols generally gave better results than vendor recommended protocols for the Ventana PATHWAY® and Dako HercepTest™. However, modifications must be meticulously validated by the end-users on a large cohort of breast carcinomas (see ASCO/CAP 2013 guidelines).
HER2 ISH module - run H15
HER2 ISH: 122 labs participated, 72% sufficient, 50% optimal. Despite optimal protocol settings, a high proportion of technical insufficient results were seen, indicating that technical issues are influencing the quality of the BRISH assays. Thus, the most commonly used HER2 BRISH assay, INFORM™ HER2 Dual ISH (Ventana/Roche), only provided a pass rate of 71% despite using appropriate, well-characterized protocol settings.
April 17th 2019
Mogens Vyberg
Scheme director
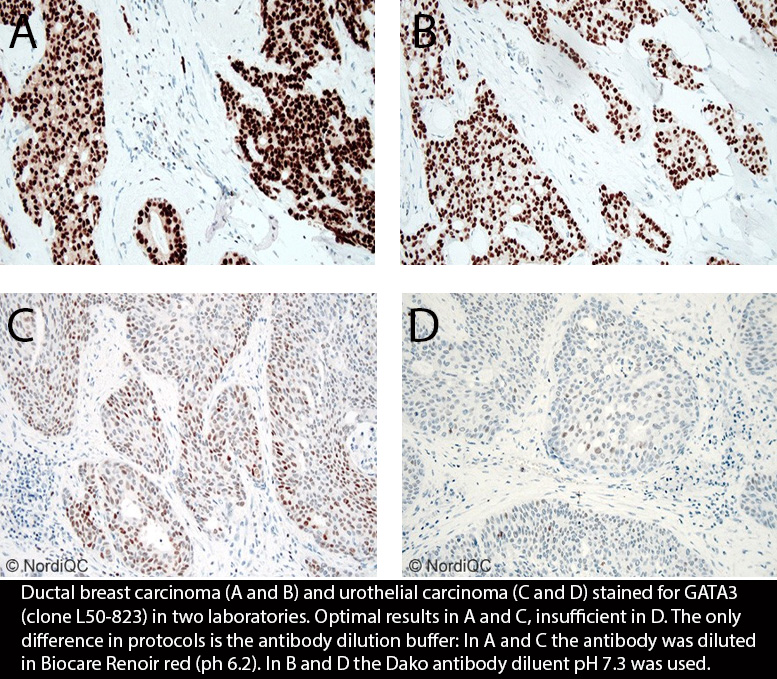
Run 54 (General module), B26 (Breast cancer IHC module), H14 (HER2 ISH module) and C4 (Companion module) was accomplished September to December 2018. A very short summary of the results is given below. Click on the epitope name to see the complete general assessment results for each marker, including major causes of insufficient results, immunohistochemical critical assay performance controls (iCAPCs), and recommendable clones and protocols. Individual results are available after login on the homepage.
General module - run 54
Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA): 272 labs participated, 63% sufficient, 37% optimal. The mAb clones CEA31 and COL-1 give high performance irrespective of stainer platform. While the mAb clone II-7 showed significantly lower analytical sensitivity. Heat induced epitope retrieval in an alkaline buffer, careful calibration of the primary antibody anduse of sensitive 3-step multimer/polymer detection systems were generally important prerequisites for an optimal staining result.The mAb clone TF3H8-1 (Ventana, 760-2507) cross reacts with other protein and should not be used.
CD8: 262 labs participated, 65% sufficient, 52% optimal. Many mouse monoclonal antibodies may give optimal results, provided an optimally calibrated protocol. In contrast,the majority of assays based on the rmAb clones SP16 and SP57, both as concentrated formats or RTU systems, were challenged by false positive staining reaction in epithelial cells hindering interpretation of the specific signal for CD8.
GATA3: 245 labs participated, 76% sufficient, 50% optimal. Used within a LD-assay, the performance of the mAb L50-823 was significantly influenced by the company/distributor of the primary Ab). Efficient HIER, preferable in an alkaline buffer, careful calibration of the primary antibody concentration and use of a sensitive detection system were the most important prerequisites for optimal staining results.
Pan Cytokeratin (CK-PAN): 296 labs participated, 62% sufficient, 38% optimal. The mAb clone cocktails AE1/AE3, alone or combined with 5D3 or PCK26, and mAb clone BS5 can all be recommended but the epitope retrieval method must be specifically tailored to the clone/cocktail applied. Applying the AE1/AE3 on the Bond platform (Leica) is challenging, and the mAb clone MNF116 should not be used due to poor performance.
Podoplanin (Podop): 225 labs participated, 64% sufficient, 36% optimal. The concentrated format of the mAb clone D2-40 could provide optimal staining results on all four main stainer platforms – Dako Autostainer, Dako Omnis, Leica Bond and Ventana BenchMark, if the protocols were optimized. In general, the performance of the Ready-To-Use systems was inferior to the laboratory developed assays The Ventana 760-4395 RTU showed low analytical sensitivity whereas the DAKO IR/IS072 RTU was troubled by false positive staining reactions on the Dako Autostainer.
Breast cancer IHC module - run B26
Estrogen receptor (ER): 355 labs participated, 70% sufficient, 31% optimal, which are markedly lower scores than in the previous four runs, probably due to more challenging tumours in the TMA. rmAb clone SP1 is a highly robust Ab performing better than rmAb clone EP1 and mAb clone 6F11.
HER2 IHC: 335 labs participated, 76% sufficient, 71% optimal. This is a decline compared to the previous run, probably due to more challenging tumours in the TMA. While the Ventana Pathway is very robust, about half of the laboratories using the Dako pAb A0485 either in the Herceptest or in a laboratory developed test, got an insufficicent resultat. Interestingly, all labs using mAb clone CB11 in a laboratory developed test with an optimal protocol got sufficient results, while those using the Oracle™ mAb clone CB11 assay, all got insufficient results.
Progesterone receptor (PR): 349 las participated, 85% sufficient, 66% optimal. The most widely used Ab clones 16, PgR 636, PgR 1294 and 1E2 could all be used to obtain an optimal result. Irrespective of the clone applied, efficient HIER and careful calibration of the primary antibody were mandatory for optimal performance. Ready-To-Use (RTU) systems and laboratory developed tetst showed a similar performance.
HER2 ISH module - run H13
HER2 ISH: 193 participated either by sending 127 labs participated, 71% sufficient, 41% optimal. Optimal demonstration and evaluation of the HER2 gene amplification status in all five cores of the multi-tissue block could be obtained by all the applied dual-colour systems and the Ventana/Roche HER2 SISH one colour system. Artefacts as silver precipitates, excessive background staining or negative areas were most likely caused by technical issues as slides drying out during the staining process or inadequate washing. Laboratories performing FISH achieved a significantly higher consensus rate for the interpretation of HER2 amplification status compared to laboratories performing BRISH.
Companion module - run C4
PD-L1 (lung): 163 laboratories participated, 86% sufficient, 57% optimal. Both the companion diagnostic PD-L1 IHC assay 22C3, SK006 Dako/Agilent, and the complementary diagnostics 28-8, SK005 Dako/Agilent, and SP263, 790-4905 Ventana/Roche as well as the LD assays for PD-L1 provided a high pass rate.
December 14th 2018
Mogens Vyberg
Scheme director
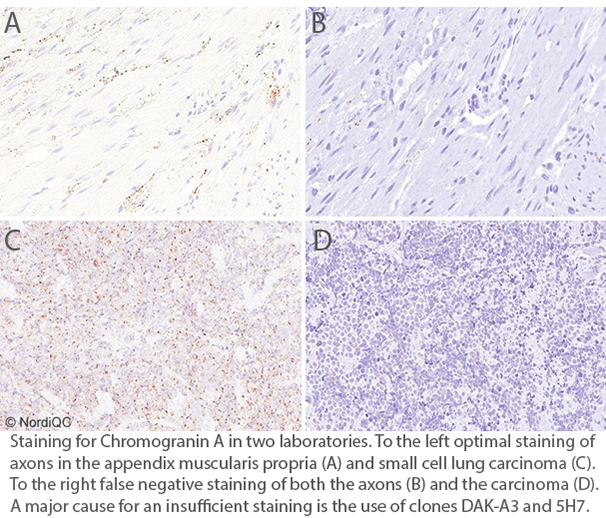
B-cell specific activator protein (BSAP, PAX5): 198 labs participated, 86% sufficient, 46% optimal. Many clones could give optimal results, best performance was seen with DAK-Pax5 (Dako/Agilent). In contrast, rmAb clone 34 (Ventana/Roche, Cell Marque) gave a very low proportion of optimal results due to a generally poor signal-to-noise ratio.
Chromogranin (CGA): 296 labs participated, 76% sufficient, 51% optimal. mAb clone LK2H10 gave superior performance, both as Conc (many companies) and RTU systems (760-2519, Ventana/Roche, and others). In contrast, mAb clone DAK-A3 as Conc (Dako/Agilent), and mAb clone 5H7, both as Conc (Leica) and RTU (PA0430/PA0515, Leica), gave unsatisfactory results.
E-Cadherin (ECAD): 298 labs participated, 89% sufficient, 65% optimal. The RTU assays based on mAb clone NCH-38 (IS/IR/GA059, Dako/Agilent) and mAb clone 36 (790-4497, Ventana/Roche) gave a high proportion of optimal results. In contrast, RTU assays based on rmAb clone EP700Y (760-4440, Ventana/Roche, and 246R-18, Cell Marque) revealed poor signal-to-noise ratios or false positive staining reactions hampering interpretation of the specific signal for ECAD.
Mismatch repair protein PMS2 (PMS2): 246 labs participated, 89% sufficient, 58% optimal. The highest proportion of sufficient staining results was seen with rmAb clone EP51 based Autostainer RTU system (Dako/Agilent) and the rmAb clone EPR3947 based Benchmark RTU system (Ventana/Roche). However, as for the latter it is noteworthy that 80 out of 83 labs (96%) modified the protocol significantly in order obtain a better staining reaction, in fact changing the RTU system to a lab developed system.
Octamer transcription factor-3/4 (OCT3/4): 189 labs participated, 94% sufficient, 83% optimal. The Conc format of the mAbs clones MRQ-10 and N1NK provided a high proportion of optimal staining results on all the four main stainer platforms: Omnis (Dako/Agilent), Autostainer (Dako/Agilent), Bond (Leica) and BenchMark (Ventana/Roche). Also the mAb clone C-10 could provide optimal staining results on all four main stainer platforms, but the proportion of optimals were significantly lower on the BenchMark and Bond compared to the Omnis and Autostainer platforms.
Reassesment for run 53 will open together with run 54, B26, H14, C4 on 1st August.
July 2018
Mogens Vyberg
NordiQC director
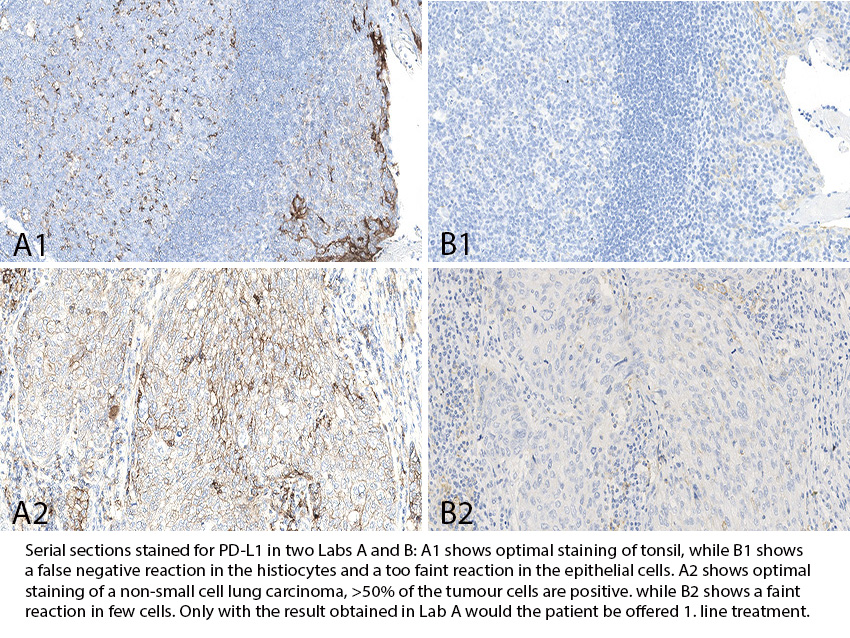
Run 52 (general module), B25 (breast cancer IHC module), H13 (HER2 ISH module) and C3 (Companion module) was accomplished December 2017 to April 2018. A very short summary of the results is given below. Click on the epitope name to see the complete general assessment results for each marker, including major causes of insufficient results, immunohistochemical critical assay performance controls (iCAPCs), and recommendable clones and protocols. Individual results are available after login on the homepage.
General module - run 52
Calretinin (CR): 269 labs participated, 72% sufficient, 45% optimal. Many clones may give optimal results. Ready-to-Use (RTU) assays generally performed better than lab developed (LD) assays indicating a need for better calibration of the latter. RTU assays should only be used on the platform for which they are developed!
MSH6: 242 labs participated, 52% sufficient, 33% optimal. Rabbit monoclonal antibodies (rmAbs) generally performed well, while the mouse monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), clone 44 and PU29 consistently failed.
Synaptophysin (SYP): 308 labs participated, 75% sufficient, 33% optimal. The lowest proportion of acceptable results both as RTU and LD assays were seen with mAbs clone SY38 (1 out of 3 sufficient) and clone MRQ-40 (9 out of 61 optimal).
Terminal deoxynucleotidyl Transferase (TdT): 225 labs participated, 82% sufficient, 39% optimal. The mAb clone SEN28 and the rmAb clone EP266 were the most successful antibodies for TdT. Efficient HIER, preferable in an alkaline buffer in combination with a sensitive and specific 3-step polymer/multimer based detection system gave the highest proportion of optimal results. Polyclonal antibodies gave virtually no optimal results.
Vimentin (VIM): 308 labs participated, 74% sufficient, 43% optimal. The mAb clones V9 and 3B4 and rmAb clone SP20, HIER in an alkaline buffer, careful calibration of the primary Ab and application of a sensitive 3-step polymer/multimer based detection system were the most important parameters for an optimal performance. The clone V9 RTU assay from Roche/Ventana (790-2917) performed less well than V9 RTU assays from other companies.
Breast cancer IHC module - run B25
Estrogen receptor (ER): 361 labs participated, 92% sufficient, 57% optimal. Both LD and RTU assays generally perform well with the mAb clone 6F11 and rmAb clones SP1 and EP1. However, as for the Leica Bond mAb 6F11 RTU (PA009/PA0151) the lab modified protocols gave better results than the vendor recommended protocols.
HER2 IHC: 342 labs participated, 96% sufficient, 81% optimal. Despite an overall improvement of LD HER2 assays from run B1 to B25, the pass rate and proportion of optimal results is still inferior to the results of FDA/CE-IVD approved systems as PATHWAY® /CONFIRM™ and HercepTest™.
HER2 ISH module - run H13
HER2 ISH: 127 labs participated, 71% sufficient, 43% optimal. Optimal demonstration and evaluation of the HER2 gene amplification status could be obtained by all the applied dual-colour and one colour systems. For the most commonly used HER2 BRISH assay, the INFORM™ HER2 Dual ISH (Ventana/Roche), a technically adequate result was provided in 65% of the slides using appropriate and vendor recommended protocol settings. A similar issue has been observed consistently in the latest NordiQC HER2 BRISH assessments, indicating a challenge for the present assay to provide a reproducible performance. As this test is used by 79% of all participating laboratories applied with appropriate protocol settings, it significantly affects the pass rate. At present, no recommendations on how to improve the end result have been identified.
Companion module - run C3
PD-L1: 146 laboratories participated, a pass rate of 91% was observed. Both the three companion diagnostic PD-L1 IHC assays 28-8, SK005 Dako/Agilent, 22C3, SK006 Dako/Agilent and SP263, 790-4905 Ventana/Roche and the LD assays for PD-L1 provided a high pass rate. However, the assessment of C3 was challenged by less than optimal material circulated. It should be emphasized that the LD assays must be carefully validated before use for diagnostics.
April 20th 2018
Mogens Vyberg
Scheme director

Run 51 (general module), B24 (breast cancer IHC module), H12 (HER2 ISH module) and C2 (Companion module) was accomplished August to December 2017. A very short summary of the results is given below. Click on the epitope name to see the complete general assessment results for each marker, including major causes of insufficient results, immunohistochemical critical assay performance controls (iCAPCs), and recommendable clones and protocols. Individual results are available after login on the homepage.
General module 51
lu-ALK (lung anaplastic lymphoma kinase): 189 labs assessed, 61% sufficient, 38% optimal. The mAb clone OTI1A4 and the rmAb clone D5F3 were the most successful Abs for demonstration of EML4-ALK translocation in lung adenocarcinoma. For mAb clone 5A4 the analytical sensitivity was significantly lower. mAb ALK1 must not be used for lung adenocarcinoma. The Ventana clone D5F3 RTU system was the most successful assay with an overall pass rate of 100% when not modified by the laboratories. HIER at high pH and use of a sensitive 3-step polymer/multimer based detection system are crucial for an optimal performance.
AMACR (α-methylacyl-CoA racemase): 250 labs assessed, 93% sufficient, 55% optimal. The rmAb clones 13H4 and SP116, mAb clone EPMU1, and pAb p504S/CP200 were all robust Abs for demonstration of AMACR. Efficient HIER in an alkaline buffer and careful calibration of the primary Ab, in combination with a sensitive IHC system (3-step polymer/multimer system), were the main prerequisites for an optimal staining result.
CD30: 282 labs assessed, 83% sufficient, 50% optimal. The mAb clones Ber-H2, CON6D/5 and JCM182 could all be used to obtain optimal staining results. Efficient HIER in an alkaline buffer or modified low pH buffer, in combination with a sensitive and specific IHC system were the main prerequisites for optimal performance.
CD117: 277 labs assessed, 63% sufficient, 25% optimal. The rmAb clones YR145 and EP10 were the most successful both in a laboratory develop (LD) assay and in an RTU format, as the overall pass rate was 94% and the proportion of optimal results was 73%. Efficient HIER in an alkaline buffer, careful calibration of the primary Ab and use of a 3-step polymer/multimer detection system provided the highest proportion of optimal results. Assays based on the pAb A4502 (Dako) were used by the majority of participants, but only 53% were sufficient and 6% optimal. A similar pattern was seen with the RTU system based on the rmAb 9.7 (Ventana), where only 53% were sufficient and 3% optimal. Both Abs are difficult to calibrate to an acceptable level.
PAX8: 213 labs assessed, 56% sufficient, 20% optimal. Optimal staining results could be obtained with the mAbs clones BC12 and PAX8/1492, the pAb 10336-1-AP, 363A and CP379 and particularly the recently introduced rmAb clones EP298, SP348 and ZR-1. The most widely used PAX8 antibody, mAb clone MRQ-50, performed satisfactory on both the Leica Bond and Dako Autostainer platforms but had a very low pass rate on the Ventana BenchMark platform, both in a laboratory develop (LD) assay and in an RTU assay. The highest proportion of optimal results was obtained performing HIER in an alkaline buffer for at least 20 min. (32 min. for Ventana BenchMark) and use of a sensitive and specific 3-step polymer/multimer based detection system.
Breast cancer IHC module - run B24
ER: 386 labs participated, 92% sufficient, 71% optimal. Both lab developed and RTU assays generally perform well with the mAb clone 6F11 and rmAb clones SP1 and EP1. However, as for the RTUs the lab modified protocols generally gave better results than the vendor recommended protocols from Dako/Agilent, Leica and VMS/Roche: Grouped together, 163 out 203 (80%) of the lab modified RTU protocols gave optimal results, compared to 50 out of 74 (68%) of vendor recommended protocols. It is noteworthy that 203 out of 277 labs (73%) found need to modify the vendor recommended protocols in order to optimize the staining reaction.
HER2 IHC: 369 labs participated, 97% sufficient, 78% optimal. Despite an overall improvement of the pass rate for lab developed HER2 assays from run B1 to B24, the pass rate and proportion of optimal results is still inferior to the FDA/CE-IVD approved systems as PATHWAY® /CONFIRM™ and HercepTest™. In general, the three FDA-/CE-IVD approved HER2 assays provided a proportion of optimal results of 85% (226 of 266), whereas only 59% (61 of 103) of LD HER2 assays were assessed as optimal. On the other hand laboratory modified RTU assays seemed to perform better than the vendor recommended: Compiling the resuls of Agilent/Dako and Roche/VMS assays, 90 of 120 (75%) stains were optimal with the vendor recommended protocols, while 119 of 131 (91%) with the laboratory modify protocols. It is noteworthy that 146 out of 266 labs (55%) found need to modify the vendor recommended protocols in order to optimize the staining reaction.
PR: 385 labs participated, 99% sufficient, 77% optimal. Both lab developed assays and RTU assays generally perform well with the most widely used Abs clones 16, PgR 636, PgR 1294 and 1E2.
Breast cancer ISH module - run H12
HER2 ISH: 115 labs participated, 64% sufficient, 37% optimal. Technically optimal demonstration of HER2 BRISH could be obtained by the commercially available two-colour HER2 systems INFORM™ HER-2 Dual ISH (Ventana) and ZytoDot® 2C (ZytoVision), and the single-colour HER2 systems INFORM™ SISH system (Ventana) and ZytoDot® (ZytoVision). For all systems, retrieval settings – HIER and proteolysis – must be carefully balanced to provide sufficient demonstration of signals and preserve morphology. Despite optimal protocol settings, a high proportion of technically insufficient results were seen, which currently cannot be explained.
Companion module - run C2
PD-L1: 145 laboratories participated, a pass rate of 84% was observed. The three companion diagnostic PD-L1 IHC assays 28-8, SK005 Dako/Agilent, 22C3, SK006 Dako/Agilent and SP263, 790-4905 Ventana/Roche were most successful providing a pass rate of 95%. Laboratory developed (LD) assays for PD-L1 provided a pass rate of 73%, (in comparison, a pass rate of 20% in C1 for this group was observed). Access to best practice protocol settings for LD assays are being developed and published supporting the implementation of LD assays. However, it must be emphasized that the LD assays must be carefully validated before use for diagnostics.
December 15th 2017
Mogens Vyberg
Scheme director

This 1st QuIP/NordiQC Workshop in Brugge, Belgium is aimed to give an update on basic and advanced immunohistochemical methods applied in diagnostic pathology, particularly for the classification of the unknown primary tumour as well as breast, lung and haematolymphoid tumours. The workshop will particularly focus on
- understanding the three phases in the technical test approach
- planning and diagnostic use of antibody panels
- optimization of staining protocols
- use of recommended tissue controls
- identification and handling of technical and diagnostic pitfalls
- image analysis of immunostains for diagnostic use
The target group comprises biomedical technicians and scientists or equivalent with some experience in immunohistochemistry, and residents and consultants in clinical and surgical pathology with special interest in the technical parts of immunohistochemistry. Maximum number of participants: 70.
Programme and practical details
Click this link for registration NB! Fully booked, you may register for the waiting list
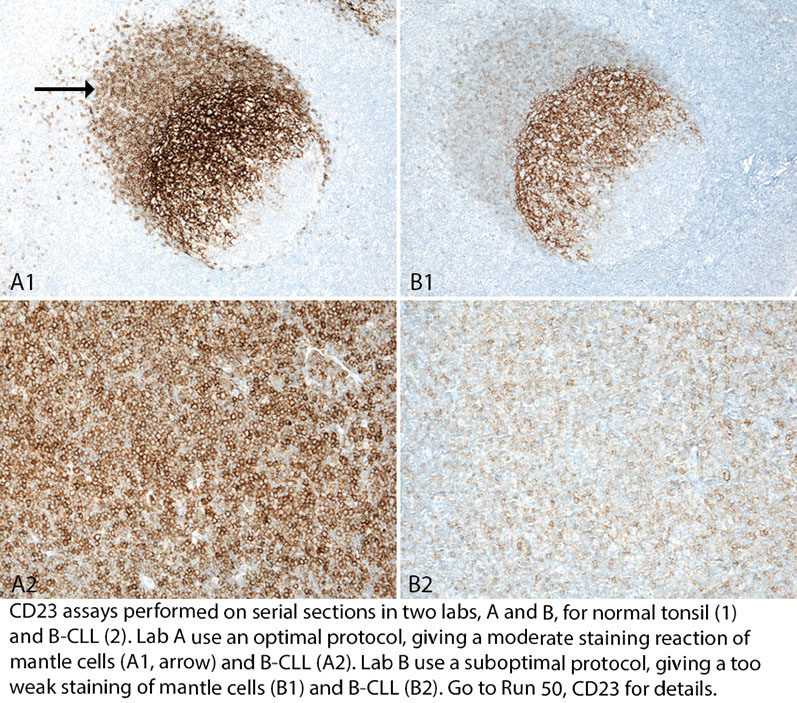
Run 50 was accomplished January to July 2017. A very short summary of the results is given below. Click on the epitope name to see the complete general assessment results for each marker, including immunohistochemical critical assay performance controls (iCAPCs), recommendable clones and protocols, as well as major causes of insufficient results.
Individual results are sent to all participants by email.
Results general module - run 50
CD23: 270 labs assessed, 89% sufficient, 55% optimal. All stains deemed insufficient showed too weak reactions. Many clones provided optimal results. Irrespective of the clone, HIER in an alkaline buffer and careful calibration of the primary Ab in combination with a sensitive 3-step detection system are critical parameters for a sufficient result. On the Ventana BenchMark platform, rmAb SP23 should be preferred rather than mAb 1B12. RTU systems for CD23 from the main IHC system providers were most successful.
CK19: 245 labs assessed, 82% sufficient, 42% optimal. HIER in an alkaline buffer, and careful calibration of the primary Ab in combination with a sensitive 3-step detection system are critical parameters for a sufficient result. Proteolytic pretreatment as single retrieval method is incompatible with an optimal result.
ERG: 130 labs assessed, 67% sufficient, 38% optimal. The prevalent feature of insufficient results was too weak or false negative staining reaction. HIER in an alkaline buffer, and careful calibration of the primary Ab in combination with a sensitive 3-step detection system are critical parameters for a sufficient result. Primary Ab selection is also important: mAb 9FY was less successful compared to rmAb clone EP111 and EPR3864. The Agilent/Dako RTU system based on rmAb clone EP111 provided the highest pass rate and proportion of optimal results.
MSH2: 231 labs assessed, 79% sufficient, 50% optimal. Most stains deemed insufficient showed too weak reactions but cases with false positive reactions or poor signal-to-noise ratio were also seen. The performance of mAb clone 25D12 was, as seen in previous asessments, inferior to mAb clones FE11 and G219-1129. mAb clone FE11 performs less well on the Ventana BenchMark platform, while with mAb G219-1129 no optimal results were seen with the Dako Autostainer and Leica Bond platforms. RTU systems for MSH2 from Agilent/Dako and Roche/Ventana were most successful.
S100: 299 labs assessed, 82% sufficient, 23% optimal. pAbs against S100 were most successful. HIER in an alkaline buffer and a careful calibration of the primary Ab are critical parameters for a sufficient result. Omission of HIER or use of proteolytic pre-treatment cannot be recommended. RTU systems based on pAbs from the main IHC providers gave relatively high pass rates, but few optimal results.
SMH: 109 labs assessed, 78% sufficient, 42% optimal. HIER in an alkaline buffer, and careful calibration of the primary Ab in combination with a sensitive 3-step detection system are critical parameters for a sufficient result. mAb clone SMMS-1 was the most widely used primary Ab and provided optimal results on all main IHC systems both within laboratory developed assays and RTU systems.
July 10th 2017
Mogens Vyberg, Scheme director

Login to see individual results
Results general module - run 49
CD5: 278 labs assessed, 92% sufficient, 68% optimal. Ready-To-Use (RTU) systems obtained superior pass rates and higher proportion of optimal results compared to laboratory developed (LD) tests. Within LD tests, optimal results required efficient HIER, preferable in alkaline buffer, and careful calibration of the primary Ab titre.
CK-LMW: 229 labs assessed, 80% sufficient, 31% optimal. The mAb clone cocktail B22.1/B23.1, rmAb clone cocktail EP17/30 and rmAb clone EP17 were the most successful antibodies for immunohistochemical demonstration of CK-LMW. In contrast mAb clone 34βH11 and in particular clones CAM5.2 are less successful and prevent improvement of the overall pass rate for CK-LMW.
MLA: 255 labs assessed, 60% sufficient, 32% optimal. The Ready-To-Use system for MLA from Dako (IR633/IS633 – AS48) based on mAb clone A103 applied according to the vendor recommended protocol settings provided the highest proportion of sufficient and optimal results. However, the clone showed less successful performance on the fully automated IHC platforms Omnis (Dako) and BenchMark (Ventana).
MLH1: 224 labs assessed, 59% sufficient, 30% optimal. Clone ES05 was most successful, both as concentrate and as RTU format (Dako/Agilent and Leica/Novocastra). The mAb clone M1 could not be used to obtain optimal staining for MHL1 due to aberrant nuclear staining in colon adenocarcinoma known to lack MLH1 expression.
NKX3.1: 49 labs assessed, 65% sufficient, 45% optimal. rmAb clone EP356 and pAb CP422 were the most successful antibodies. With LD assays, efficient HIER in an alkaline buffer and use of a sensitive and specific 3-step polymer/multimer based detection system gave the highest proportion of optimal results. Testis and normal prostate can be used as positive tissue controls
PSA: 284 labs assessed, 89% sufficient, 68% optimal. Careful calibration of the Ab concentration and sufficient HIER are required.
Results breast cancer IHC module - run B23
ER: 394 labs assessed, 92% sufficient, 56% optimal. The most used clones 6F11, EP1 and SP1 are all recommended. RTU systems obtained superior pass rates and higher proportion of optimal results compared to LD assays. For LD assays, too low concentration of the Ab and insufficient HIER were major reasons for insufficient assays.
HER-2 IHC: 372 labs assessed, 95% sufficient, 82% optimal. The FDA-/CE-IVD approved PATHWAY®/CONFIRM™ (Ventana) and HercepTest™ (Dako) were the most precise assays for the semi-quantitative IHC determination of HER-2 protein expression. LD assays produced a lower pass-rate and were less precise for the HER-2 status requiring an additional ISH test for final evaluation. Inclusion of 2+ tumours with and without HER-2 gene amplification in the control material for both EQA and internal quality control is essential to evaluate precision and performance stability of the IHC HER-2 assays used by laboratories.
Results companion module - run C1
PD-L1: 68 labs assessed, 50% sufficient, 37% optimal. Suboptimal results are mostly related to unexplained technical issues, which prevent recommendations for improvement. The Dako/Agilent 22C3 pharmDx assay SK006, applied by protocol settings in compliance with the vendor recommendations, was most successful with an overall pass rate of 92%. LD assays were used by 44% of the labs and a pass rate of 20% was seen.
Results breast cancer ISH module - run H11
HER-2 ISH: 123 labs assessed (BRISH only), 60% sufficient, 32% optimal. Suboptimal results are mostly related to unexplained technical issues, which prevent recommendations for improvement.
April 21st 2017
Mogens Vyberg
Scheme director

Runs 48/B22/H10 were accomplished from September to December 2016. A very short summary of the technical test results is given below. Click on the epitope name to see the complete general assessment results for each marker, including recommended clones and protocols, as well as major causes of insufficient staining results, and for HER2 IHC/ISH and Ki67 also concordance of interpretation. Individual results are available for the participants by logging in.
Results general module - run 48
CDX2: 268 labs assessed, 80% sufficient, 58% optimal. Careful calibration of the Ab concentration and a sensitive visualization system are required. The old clones CDX-88 and AMT28 cannot be recommended. DAK-CDX2 should not be applied on the Ventana BenchMark platform.
Desmin (DES): 275 labs assessed, 87% sufficient, 48% optimal. Efficient Heat induced epitope retrieval (HIER) and a sensitive detection system are mandatory for an optimal result. Clone D33 should not be used on the Dako Omnis platform. RTU VMS mAb DE-R-11 (760-2513 for Ultra/XT) performed better with laboratory modified protocols than with the vendor recommended protocol (61% vs 0% optimal). In contrast RTU Dako mAb D33 (IR606/IS606 for AS48) performed better with the vendor recommended protocol than with laboratory modified protocols (80% vs 57% optimal).
MUM1: 211 labs assessed, 60% sufficient, 40% optimal. Efficient HIER, careful calibration of the Ab concentration and a sensitive visualization system are required for optimal performance. The clones rmAb MRQ-43, mAb MRQ-8 and mAb BC5 all produce insufficient results and cannot be recommended.
p40: 188 labs assessed, 74% sufficient, 42% optimal. Careful calibration of the Ab concentration and a sensitive visualization system are required. Polyclonal Abs cannot be recommended. RTU VMS mAb BC28 (790-4950 for Ultra/XT) performed better with laboratory modified protocols than with the vendor recommended protocol (57% vs 40% optimal).
p63: 274 labs assessed, 82% sufficient, 44% optimal. Efficient HIER, careful calibration of the Ab concentration and a sensitive visualization system are required for optimal performance. Clone 7JUL cannot be recommended, as almost all labs failed with this clone. RTU VMS mAb 4A4 (790-4509 for Ultra/XT) performed better with laboratory modified protocols than with the vendor recommended protocol (60% vs 20% optimal).
SOX10: 121 labs assessed, 68% sufficient, 50% optimal. Careful calibration of the Ab concentration and a sensitive visualization system are required. Polyclonal Abs cannot be recommended.
Results breast cancer IHC module - run B22
HER2 IHC: 387 labs assessed, 84% sufficient, 71% optimal. Pathway®/ConfirmTM (Ventana) and HercepTestTM (Dako) gave pass rates above 90% while the pass rates for OracleTM (Leica) and the laboratory developed kits were too low. Several labs are using approved systems off-label, which gives a lower pass rate and should be omitted, also for legal reasons.
Ki67: 409 labs assessed, 93% sufficient, 69% optimal. Efficient HIER and careful calibration of the primary Ab concentration are mandatory. RTU systems gave a higher pass rates than laboratory developed protocols. MIB-1 showed an inferior performance on Bond, Leica.
Results breast cancer ISH module - run H10
HER2 ISH: 118 labs assessed (BRISH only), 68% sufficient, 32% optimal. Suboptimal results are mostly related to unexplained technical issues, which prevent recommendations for improvement.
December 9th 2016
Mogens Vyberg
Scheme director

Runs 47 was accomplished April to July 2016. A very short summary of the tests is given below. Click on the epitope name to see the complete general assessment results for each marker, including recommended clones and protocols, and major causes of insufficient staining results. Individual results will be sent to participant by email.
Figure: Serial sections of GIST stained for CD117 in two labs. Left: optimal, right: false negative due to an insufficient protocol.
CD117: 272 participants, 47% sufficient, 14% optimal. Best results were obtained with rmAb clones YR145 and EP10, both as concentrates and in RTU formats, while pAb 4502 (Dako) gave less satisfactory results, and rmAb clone 9.7 (RTU 790-2951, Ventana) performed poorly. HIER in an alkaline buffer in combination with careful calibration of the primary Ab were the most critical parameters for a sufficient result. See photo above
CEA: 255 participants, 42% sufficient, 17% optimal. Best results were obtained with mAb clones CEA31 (both as concentrates and in RTU formats) and COL-1 (as concentrate). mAb clone II-7 gave less satisfactory results (particularly on the Ventana Benchmark platform), and mAb clone TF3H8-1 (RTU 760-2507, Ventana) performed poorly. Optimal results could only be obtained with use of HIER in an alkaline buffer. The tissue material was more challenging than in previous runs, but the causes of sufficient and insufficient results are basically the same.
CK20: 284 participants, 92% sufficient, 62% optimal. Efficient HIER is recommended, proteolytic pretreatment generally gives a lower pass rate.
CK-PAN: 275 participants, 72% achieved a sufficient mark, 48% optimal. For Ab cocktails containing AE1/AE3 HIER is mandatory. mAb MNF116 requires proteolytic pretreatment but the clone performs less well than AE1/AE3.
CyD1: 257 participants, 94% sufficient, 54% optimal. Both rmAb clones EP12 and SP4 can be recommended. However, SP4 performed less optimal on the Bond platform.
SOX11: 79 participants, 66% sufficient, 27% optimal. mAb clones MRQ-58 and SOX11-C1 can both be recommended. However, clone MRQ-58 in RTU format from Ventana (760-4888) works better with OptiView than UltraView (that is receommended by the producer).
Run 48, B22, H10 opens for protocol submission on 12th August.
July 11th 2016
Mogens Vyberg
Scheme director

